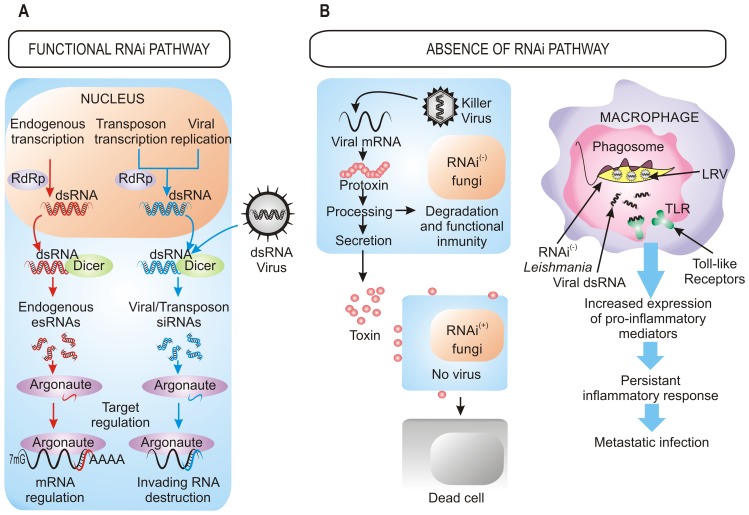
Figure 1. Benefits of the retention/loss of the RNAi pathway.
(A) Cellular processes dependent on RNAi machinery. In organisms with a functional RNAi pathway, it plays a central role in the destruction of invading viral RNA, the elimination of transcripts from transposons, and the regulation of the expression of endogenous genes by small RNAs generated within the cell. (B) Viral pressure as a selective force for the loss of RNAi in fungi and parasites. The presence of dsRNA killer viruses in several RNAi-deficient fungi confers a selective advantage to these species over those with RNAi functional pathways (left). In Leishmania RNAi-deficient strains, the presence of dsRNA viruses (LRV) modifies the course of the infection, provoking an enhanced inflammatory response that results in a higher parasite burden (right). (+): functional RNAi pathways, (−): absence of RNAi pathways.