Figure 3. Entry of C. burnetii, but not S. Typhimurium or C. trachomatis, is reduced in the absence of cholesterol.
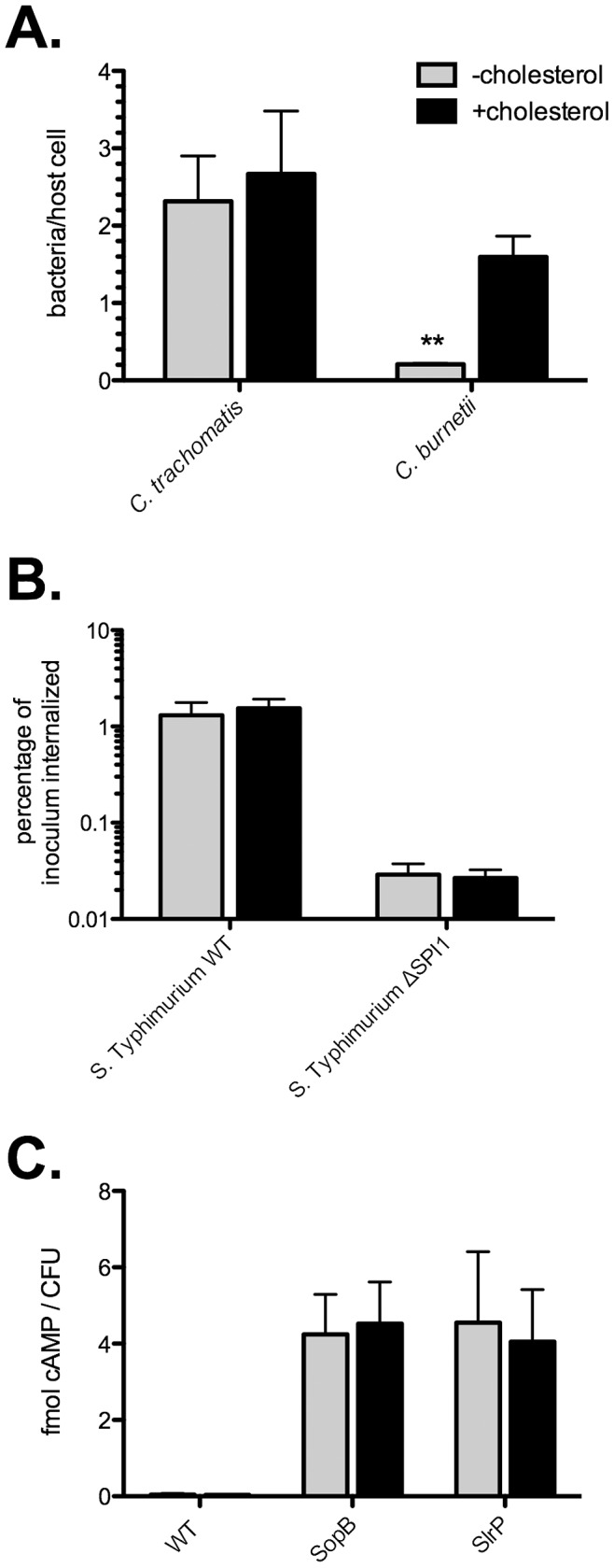
Entry assays were performed to test the ability of C. trachomatis, C. burnetii, and S. Typhimurium to enter host cells in the absence of cholesterol. (A). The number of internalized C. trachomatis was unchanged between −cholesterol and +cholesterol MEFs. In contrast, internalization of C. burnetii was decreased by 87% (p = 0.0009) in −cholesterol MEFs. Error bars indicate the standard deviation from the mean of three independent experiments, each done in triplicate. (B). Wild type (WT) S. Typhimurium and a mutant lacking the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (ΔSPI1) invaded −cholesterol and +cholesterol cells with equal efficiency. (C). CyaA assay showing robust translocation of the S. Typhimurium type III effectors SopB and SlrP in both -cholesterol and +cholesterol MEFs. Normal cAMP levels were observed following infection with WT bacteria not expressing the fusion proteins (negative control). Error bars indicate the standard deviation from the mean of three independent experiments, each done in triplicate.
