Figure 4. C. burnetii utilizes αVβ3 integrin for uptake in a cholesterol-dependent manner.
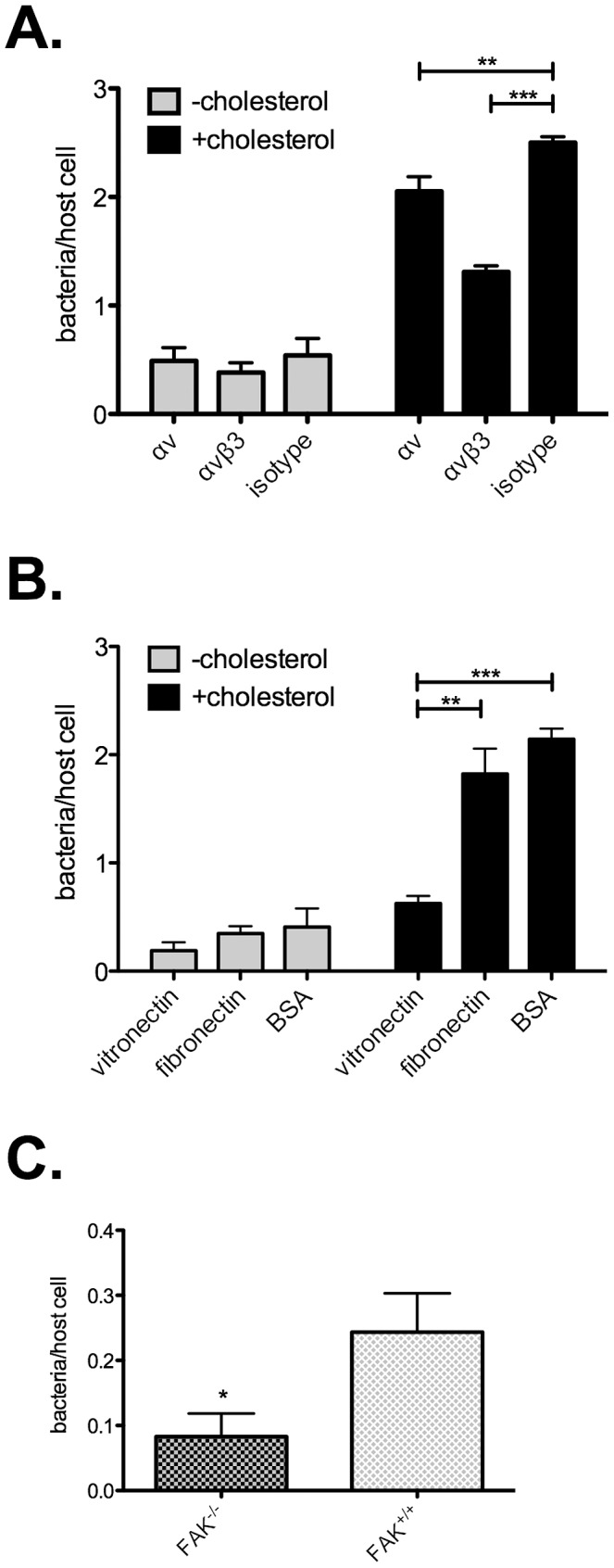
(A). Entry assays in the presence of αVβ3 integrin blocking antibodies. C. burnetii internalization by −cholesterol MEFs was not significantly altered. In contrast, blocking either αV integrin or αVβ3 integrin in +cholesterol MEFs blocked C. burnetii entry by 18% (p = 0.0061) and 48% (p<0.0001), respectively. (B). When +cholesterol cells were pre-incubated with vitronectin, the major ligand for a αVβ3 integrin, C. burnetii entry decreased by 66% (p = 0.001) and 71% (p<0.0001) as compared to pre-incubation with fibronectin or BSA, respectively. No effect was seen on −cholesterol MEFs. (C). Cells lacking the downstream αVβ3 integrin signaling protein focal adhesion kinase (FAK) were tested for C. burnetii entry. As compared to wild type FAK+/+ cells, internalization decreased by 66% (p = 0.0160) in FAK−/− cells. Error bars indicate the standard deviation from the mean of three independent experiments, done in triplicate.
