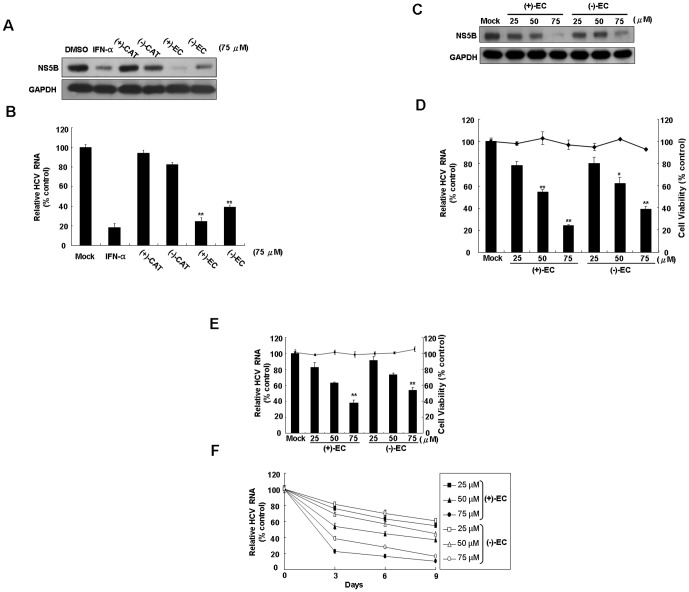
Figure 1. Anti-HCV activity of phenolic CATs.
Inhibitory effect of various phenolic CATs on HCV (A) protein synthesis and (B) RNA replication. Concentration-dependent reduction of HCV (C) protein synthesis and (D) RNA replication in (+)-EC- or (−)-EC-treated HCV replicon cells. Ava5 cells were treated with each CAT isomers [(+)-CAT, (−)-CAT, (+)-EC and (−)-EC] at the indicated concentrations (25, 50, and 75 µM). After 3 days, the cell lysates were collected and then subjected to Western blotting with antibodies against NS5B and GAPDH (loading control). IFN-α (100 U/mL) and DMSO (0.1%) treatment served as the positive and mock controls, respectively. HCV RNA levels was quantified by qRT-PCR and normalized to gapdh mRNA levels after CAT isomers treatment for 3 days. Cellular toxicity was evaluated by the MTS assay after 3 days in the presence of the indicated concentrations of each EC isomers. (E) Concentration-dependent reduction of infectious HCV JFH-1 replication in (+)-EC- or (−)-EC-treated Huh-7.5 cells. After 6 h of JFH-1 virus incubation, Huh-7.5-infected cells were treated with EC isomers for 3 days. The levels of intracellular HCV RNA were determined by qRT-PCR following normalization of cellular gapdh mRNA. The efficacy of inhibition is expressed as the percentage relative to the RNA levels quantified without ECs (mock control). (F) Time-dependent reduction of HCV RNA levels in Ava5 cells treated with EC isomers. Ava5 cells were treated with EC isomers at concentration of 25, 50 and 75 µM. HCV RNA levels were quantified by qRT-PCR after EC isomers treatment for 3, 6 and 9 days. DMSO (0.1%) treatment served as the mock controls. Error bars represent the SD from three experiments. *P<0.05; **P<0.01.