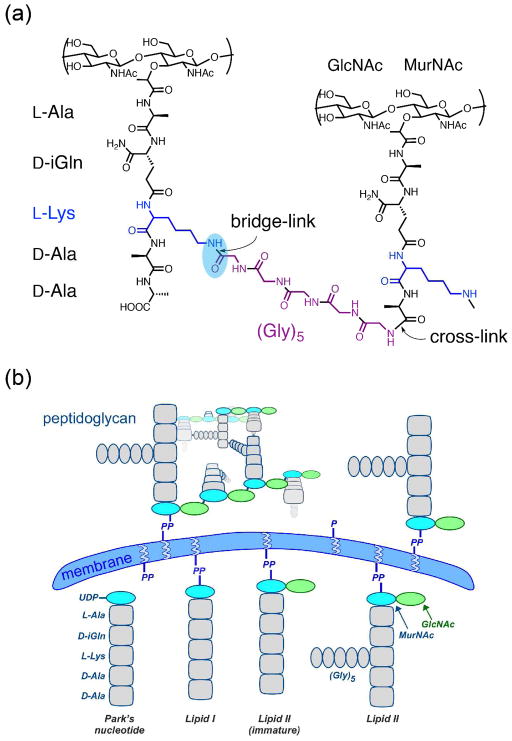
Figure 1. Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan.
(a) Chemical structure of S. aureus peptidoglycan, which is cross-linked through an inter-peptide bridge consisting of five glycines to connect the ε-amino group of L-Lys in the third position of one stem (bridge-link, highlighted) to the D-Ala in the fourth position of the connected stem (cross-link) with the concomitant cleavage of the terminal D-Ala. (b) Assembly pathway of S. aureus peptidoglycan. The peptidoglycan precursor lipid II is assembled inside the cell with pentaglycine bridge attached and is “flipped” outside the cell to be incorporated into the peptidoglycan network through transglycosylation (to connect the glycan strands) and transpeptidation (to cross-link the peptides).