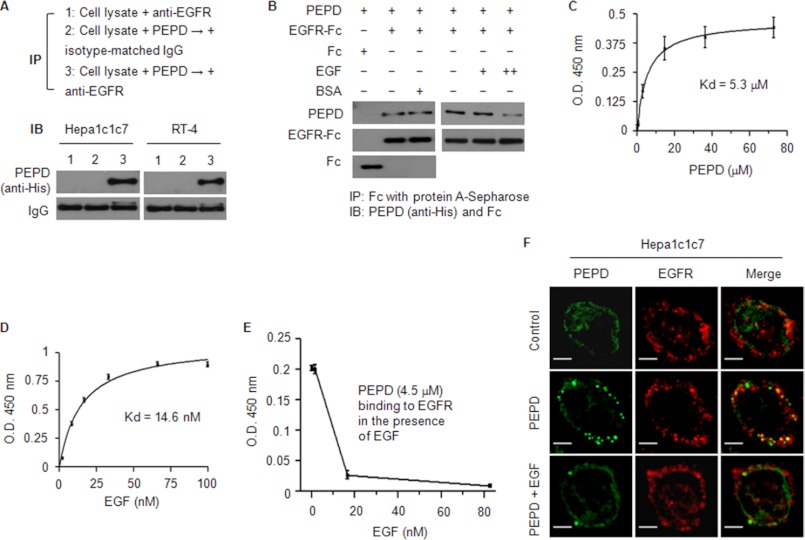
FIGURE 2.
PEPD binds to EGFR. A, cell lysates (1 mg of protein/ml) were incubated with PEPD (40 μg/ml) for 1 h at 37 °C and then incubated with anti-EGFR or an isotype-matched IgG overnight at 4 °C. As a control, an equal amount of cell lysates were incubated with anti-EGFR without prior incubation with PEPD. All samples were then subjected to pull-down by protein G-Sepharose beads and Western blotting for PEPD. B, PEPD (0.4 nmol/ml) was incubated with EGFR-Fc (0.04 nmol/ml), EGFR-Fc (0.04 nmol/ml) plus BSA (19 nmol/ml), or Fc (0.04 nmol/ml) for 1 h at 37 °C and then overnight at 4 °C. In a separate experiment, PEPD (1 nmol/ml) was incubated with EGFR-Fc (0.04 nmol/ml) in the absence or presence of EGF (+, 5 pmol/ml; ++, 50 pmol/ml) for 1 h at 37 °C and then overnight at 4 °C. All samples were then subjected to pull-down by protein A-Sepharose beads and Western blotting for PEPD, Fc, and/or EGFR-Fc. C–E, binding of PEPD or EGF to EGFR or inhibition of PEPD-EGFR binding by EGF, measured by an ELISA as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Each value is mean ± S.D. The Kd values were estimated by nonlinear regression (GraphPad Prim 4 Software, r2 > 0.99). F, cells were incubated with 0.27 μm PEPD (with or without 0.027 μm EGF) or vehicle (same as in the PEPD/EGF groups) for 4 h, and after paraformaldehyde fixing and BSA blocking, were incubated with anti-EGFR and then a phycoerythrin-conjugated secondary antibody and FITC-conjugated anti-His, followed by confocal microscopy. Bar, 10 μm.