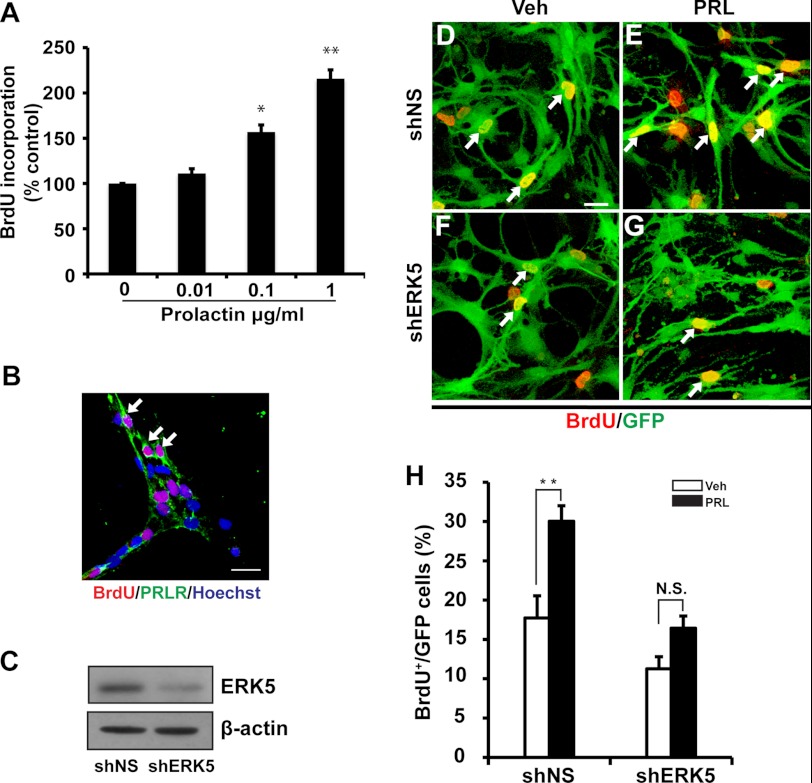
FIGURE 4.
Retroviral shRNA knockdown of ERK5 attenuates prolactin-induced proliferation in SVZ-aNPCs. A, prolactin treatment (18 h) induced SVZ-aNPC proliferation in a dose-dependent manner, measured by BrdU incorporation. B, immunocytochemistry showed that prolactin receptor (PRLR, green) is expressed in cells incorporating BrdU (red). C, Western analysis demonstrating that retrovirus expressing shRNA against ERK5 (shERK5) suppresses the expression of endogenous ERK5 in SVZ-derived aNPCs. shNS: retroviruses encoding nonspecific shRNA control. β-Actin was used as a loading control. D–G, representative fluorescence photomicrographs. Cells were infected with shNS (D, E) or shERK5 (F, G). Three days after retroviral infection, cells were treated with vehicle (Veh, D, F) or prolactin (PRL, 1 μg/ml, E, G) for 18 h followed by a 3 h BrdU incorporation (red). Virus-infected cells were identified by GFP immunostaining (green). Scale bar: 25 μm. H, quantification of data from panels D–G, as the percentage of BrdU+ cells in total GFP+ population. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; n.s. not statistically significant.