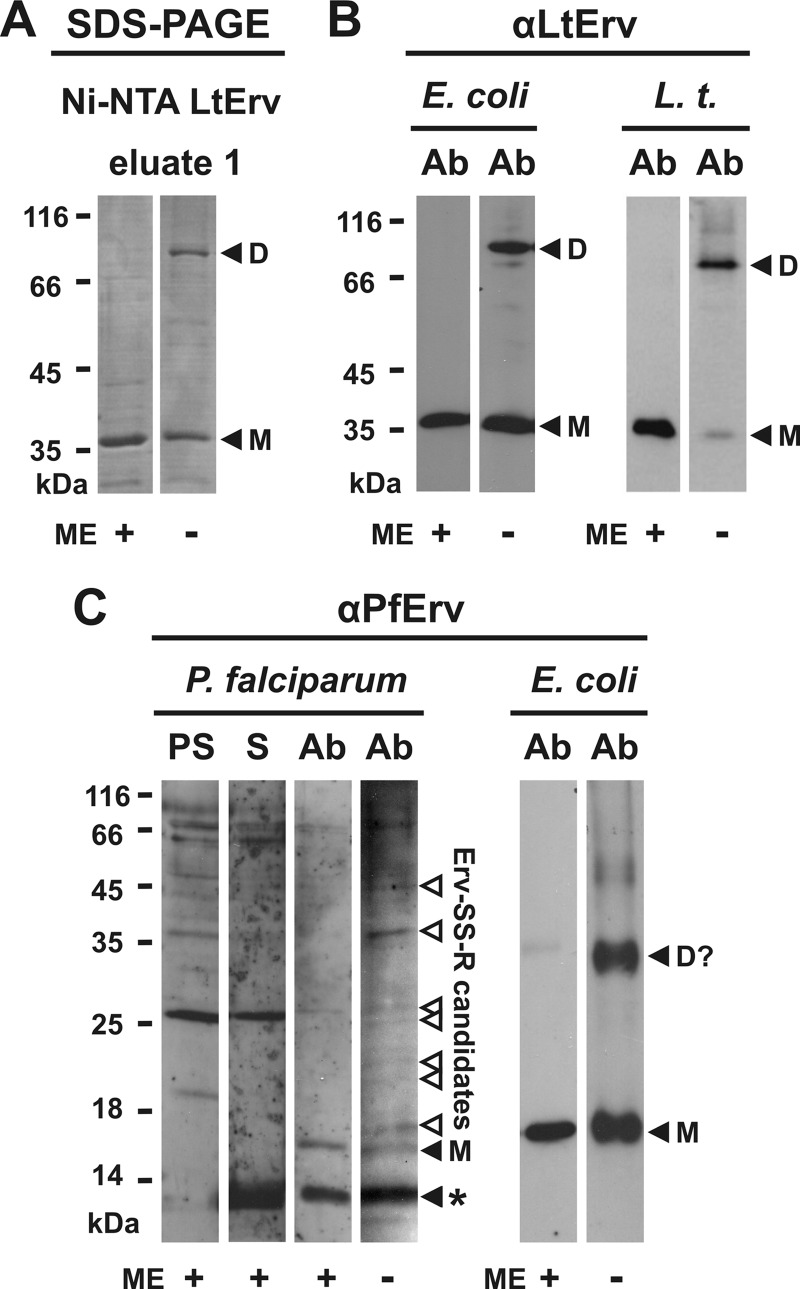
FIGURE 4.
Intermolecular disulfide bond formation of LtErv and PfErv. A, detection of disulfide-bridged homodimers of purified full-length LtErv (Fig. 3A) by non-reducing SDS-PAGE is shown. B, Western blot analyses are shown for recombinant and endogenous disulfide-bridged LtErv dimers in E. coli extracts (E. coli) and purified mitochondria from L. tarentolae (L.t.), respectively. E. coli cells were centrifuged and directly boiled in the corresponding Laemmli buffer. C, shown are Western blot analyses of endogenous and recombinant disulfide-bridged PfErv in extracts from P. falciparum and E. coli, respectively. Recombinant PfErv has a theoretical molecular mass of 18.4 kDa. Truncation of the presumably flexible N terminus of native PfErv (Table 1) results in a protein with a theoretical molecular mass of ∼13 kDa. The band labeled with an asterisk could, therefore, be either a nonspecific cross reaction or proteolytically processed PfErv. Ab, affinity purified antibody. D, dimer; D?, potential dimer; M, monomeric full-length LtErv; ME, 2-mercaptoethanol; PS, preimmune serum; S, serum.