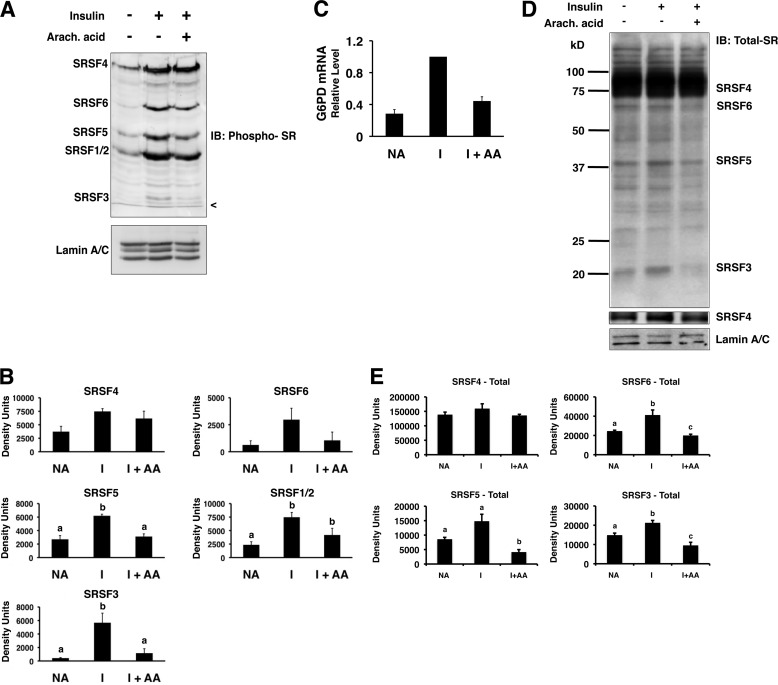
FIGURE 1.
Insulin and arachidonic acid regulate the amount of phosphorylated SR proteins in the nuclei of primary rat hepatocytes. Primary rat hepatocytes were incubated in high glucose (27.5 mm) medium alone (NA), insulin (I; 80 mm), or insulin plus arachidonic (Arach.) acid (175 μm). After 24 h, nuclear extract was prepared and analyzed by Western blotting. A, a representative immunoblot (IB) using an antibody against phosphorylated SR proteins (mAB104) and an antibody against lamin A/C is shown. The identities of the SR proteins are listed on the left side of the gel. The < symbol indicates the dye front of the gel. B, quantitation of the immunoblot data from n = 4 independent hepatocyte isolations. The amounts of the phosphorylated SR proteins in each treatment were measured by densitometry. C, total RNA was isolated from the hepatocytes after 24 h with the indicated treatments, and the amount of G6PD mRNA was measured by real time RT-PCR. The value for the amount of G6PD mRNA with insulin treatment (1.5 ± 0.3; n = 3) was set at 1, and the values for treatments with medium alone and for those with insulin plus arachidonic (Arach.) acid (I+AA) are expressed relative to the insulin treatment. D, representative immunoblots using antibodies against total SR proteins (16H3; to detect SRSF4, SRSF5, SRSF6, and SRSF3) or lamin A/C are shown. A second panel shows SRSF4 at a lighter exposure. The identities of the detected proteins are listed on the right side of the gels. E, quantitation of the immunoblot data from three independent experiments. The amounts of the SR proteins in each treatment were measured by densitometry. Columns with different letters are significantly different (p < 0.05).