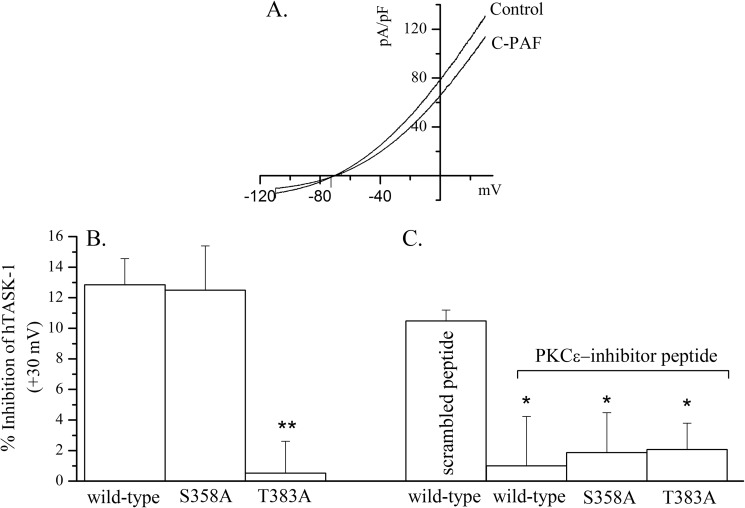
FIGURE 4.
PKCϵ-dependent inhibition of TASK-1 by C-PAF is abrogated by mutation of threonine 383 to alanine. Human TASK-1 was expressed in CHO cells, and the C-PAF-sensitive current was calculated from patch clamp recordings in the presence or absence of C-PAF (187 nm). A depicts a typical current-voltage relation for TASK-1 current under control conditions and in the presence of C-PAF. B, two TASK-1 mutants (S358A and T383A) were generated by site-directed mutagenesis and expressed in CHO cells, and the resulting currents were measured by patch clamp recording. The mean current value (± S.E.) at +30 mV was calculated for each construct. Mutation of serine 358 (n = 11) had no effect on the C-PAF-dependent inhibition of current compared with wild type (n = 9), whereas the C-PAF-dependent inhibition of the threonine mutant (n = 14) was significantly less than both wild type and S358A (**, p < 0.01). C, PKCϵ-specific inhibitory peptide (or a scrambled control peptide) was dialyzed into the cells through the patch pipette, and then the inhibition of TASK-1 current was measured in the presence or absence of C-PAF. The control peptide had no effect on the C-PAF-sensitive TASK-1 current. In contrast, inhibition of PKCϵ significantly reduced the C-PAF-dependent inhibition in all previously responsive constructs (*, p < 0.05).