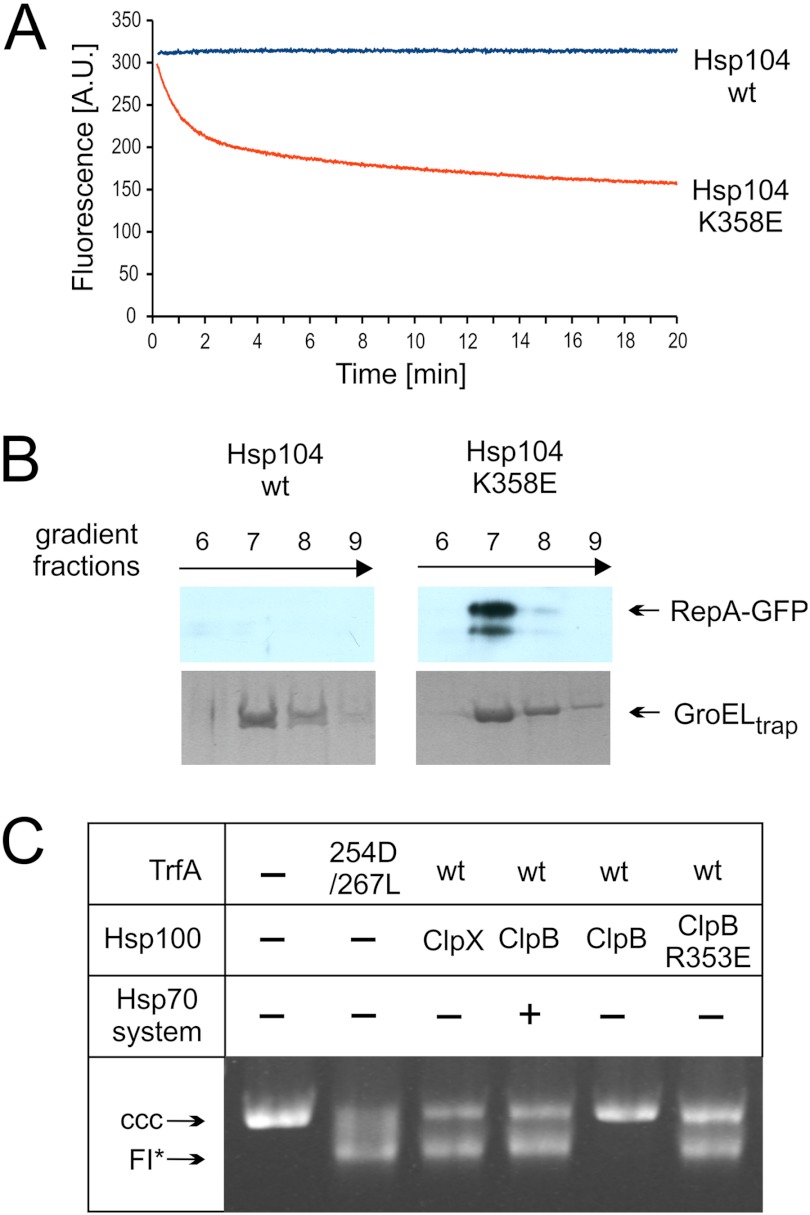
FIGURE 9.
Hyperactive Hsp100 variants unfold native proteins. A, unfolding of RepA1–70-GFP by the Hsp104 K358E variant and wt Hsp104 is shown. At time 0 the indicated variant of Hsp104 was added to the fluorimetric cuvette containing RepA1–70-GFP, and GroELtrap. GFP fluorescence was recorded. A.U., absorbance units. B, RepA1–70-GFP polypeptide was recognized by GroELtrap as a result of hyperactive Hsp104 variant unfolding of native protein. Sedimentation (16-h) of protein complexes formed after the addition of Hsp104 variants to the reaction containing RepA1–70-GFP and GroELtrap. Fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by a Western blot for RepA1–70-GFP and Coomassie Brilliant Blue for GroELtrap. C, hyperactive ClpB R353E, but not wild type ClpB, activates dimeric TrfA in the absence of the Hsp70 chaperone system. TrfA replication protein activity was determined using a reconstituted purified protein system and a helicase-dependent DNA unwinding assay with a supercoiled plasmid DNA template. Formation of FI*, an extensively unwound covalently closed circular (CCC) DNA form, depends upon TrfA-dependent origin opening and helicase loading. Chaperone proteins (ClpB and variants (2 μm), ClpX (1.6 μm), DnaK (2.2 μm), DnaJ (0.4 μm), and GrpE (1.2 μm)) were present in the reactions as indicated.