Figure 3.
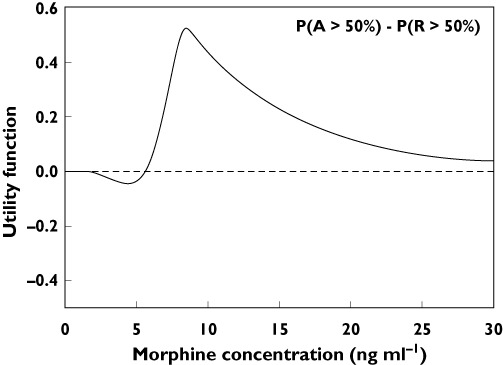
Utility function of morphine showing the probability of an analgesic effect [P(A)] greater than 50% [P(A > 50%)] minus the probability of toxicity (in this case respiratory depression) greater than 50% [P(R > 50%)]. A negative value indicates that the probability for toxicity is larger than the probability for analgesic efficacy. The reverse is true for a positive value of the utility function. For morphine at low dose the probability for respiratory depression exceeds that of analgesia, at doses >5 ng ml−1 the probability for analgesia is greater. At high morphine concentrations no differences in probability are apparent (value of the utility function approaches zero). Analgesia and respiratory data are obtained in healthy volunteers
