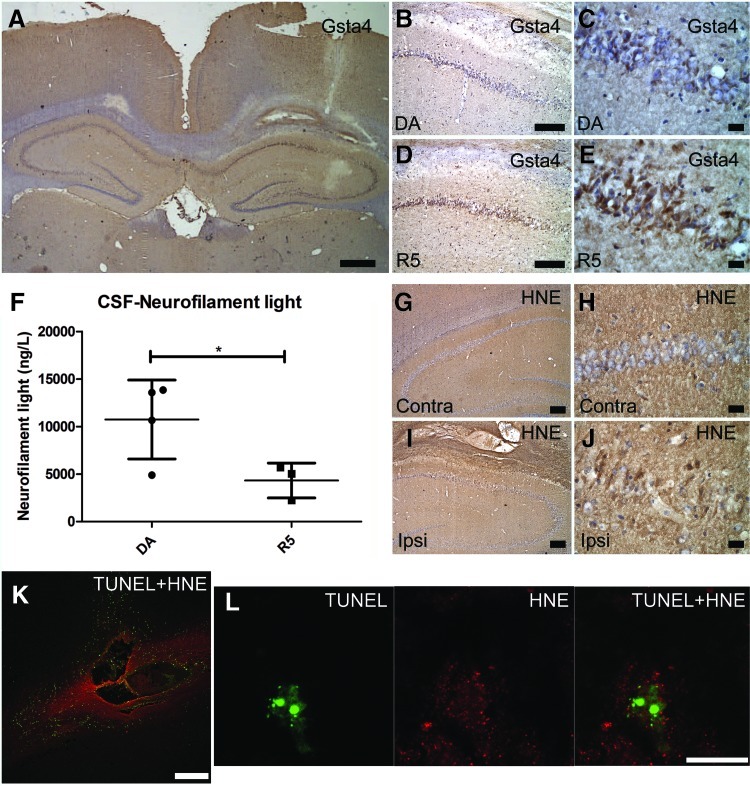
FIG. 6.
Gsta4 expression, 4-HNE detoxification, and apoptotic cell death following intracerebral 4-HNE injection. (A–E) Gsta4 immunohistochemical staining, 24 h after intraparenchymal injection of 4-HNE showing expression of Gsta4 in the site ipsilateral to the injection versus the contralateral site and differences between the DA and R5 strain particularly in the CA1 area. (F) CSF levels of neurofilament light as assessed with ELISA, and (G–J) imunohistochemical detection of 4-HNE-protein adducts in the ipsilateral versus the contralateral site. (K, L) Double immunofluorescent labeling for apoptotic cell death as assessed with TUNEL (green) and 4-HNE-protein adducts (red). Note the upregulation of Gsta4 around the injection site (A) and that neurons of the CA1 area display more Gsta4 staining for the R5 strain compared to the DA (B–E). Also, note in (F) that CSF neurofilament light levels are elevated in the DA strain compared to the R5. Furthermore, in (G–I) note that 4-HNE has diffused in the tissue surrounding the injection to form adducts which are present both in glia and neurons. Finally, (K) shows that injection of 4-HNE results in apoptotic cell death around the injection site and (L) shows a neuron of the CA1 area with an apoptotic fragmented nucleus and the presence of 4-HNE-Michael adducts in the cytoplasm. Scale bars are 1 mm in (A); 250 μm in (K), 100 μm in (B), (D), (G), and (I); 15 μm in (C), (E), (H), (J), and (L). Comparison between the two groups were evaluated by the Student's t test (*p<0.05). (To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars.)