Figure 1.
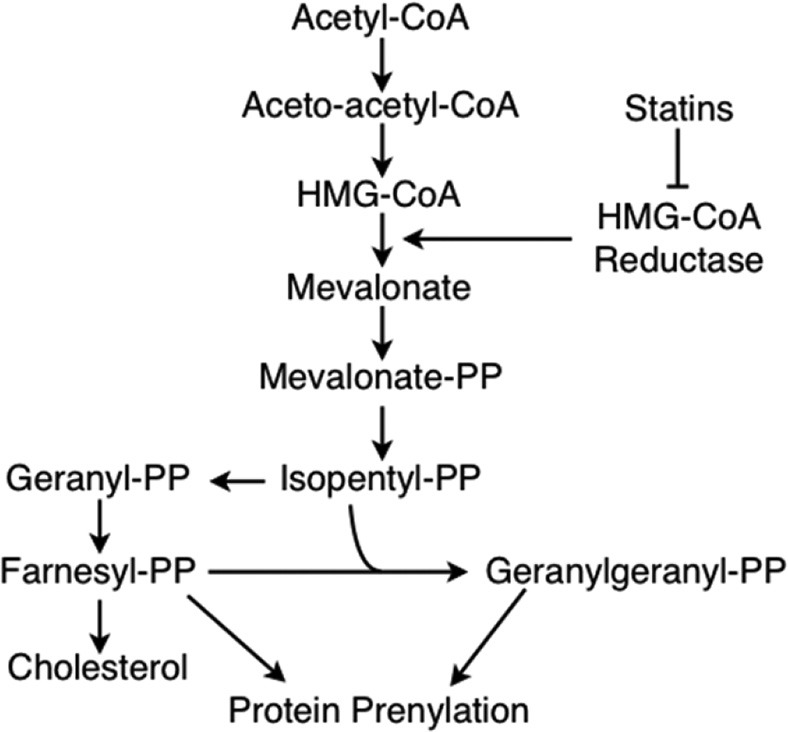
Statin mechanism of action. Statins are competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme which mediates the rate-limiting step of mevalonate production during cholesterol biosynthesis. In addition to cholesterol, this pathway also generates the isoprenoid intermediates, farnesyl pyrophosphate (PP) and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate. Both of these products are used in post-translational modification of proteins via prenylation.
