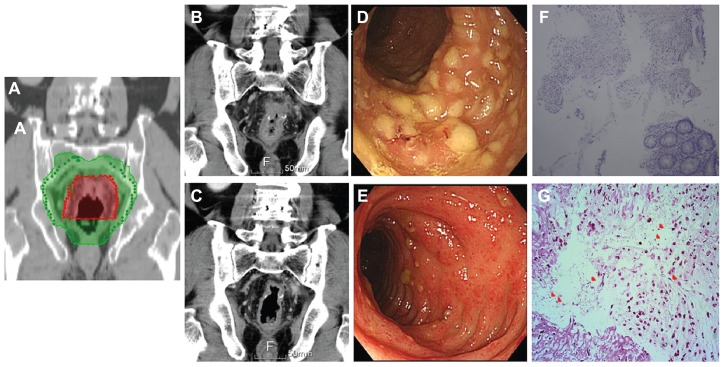
Figure 1.
(A) The irradiation fields in radiation plan. Fifty-four Gray (Gy) and 50 Gy was delivered in red and green area, respectively. (B) The first evaluative CT scans after concurrent chemoradiation therapy. Inflammation of the sigmoid colon showing infiltrative changes around the site of anastomosis, edematous changes on the serosal surface, and marked thickening of the colonic wall. (C) The second evaluative CT performed at 3-month follow-up reveals mild inflammatory changes around the anastomotic site. (D) Endoscopic examination showed multiple white and yellow pseudomembranes on the wall of the rectum, as well as swelling, suggesting pseudomembranous colitis. (E) After a 2-week course of antibiotics, the number of pseudomembranes decreased and the severity of diarrhea gradually improved. (F) Histolopathologic analysis revealed partial or full thickness necrosis of the mucosa, glandular hypersecretion, and pseudomembranes composed of fibrin, mucus, and inflammatory cells (hematoxylin and eosin stain, ×100), findings suggestive of pseudomembranous colitis. (G) Gram-positive bacilli were identified in the suppurative exudate over the colonic mucosa (red arrows, Gram stain, ×400).