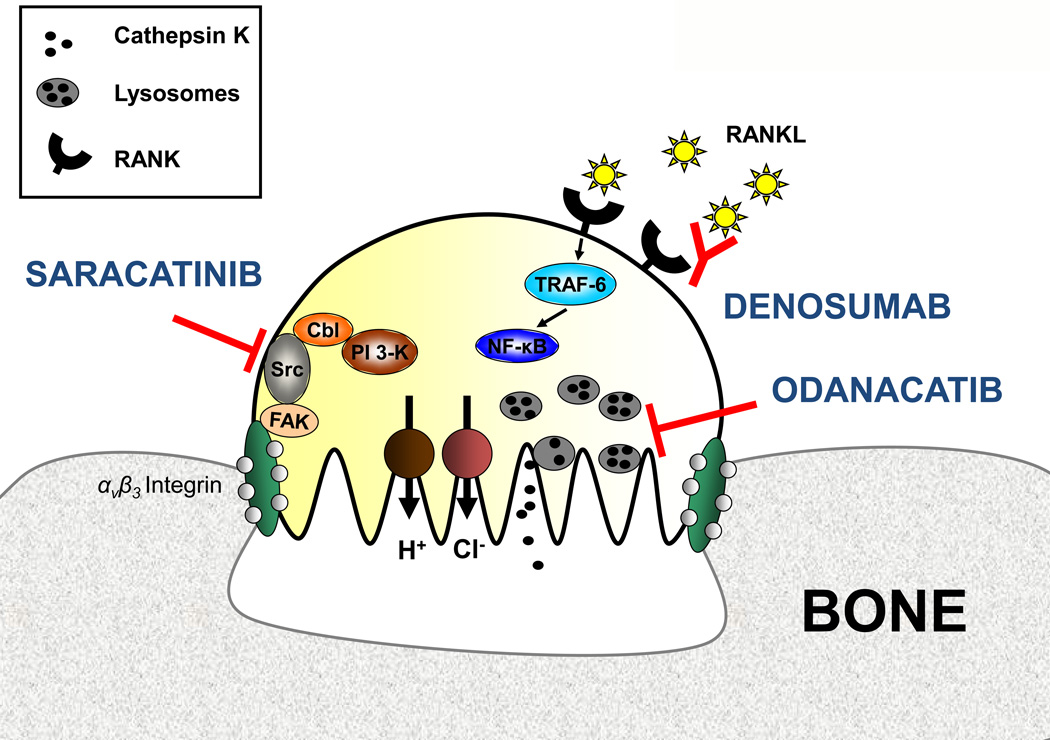
Figure 2. Osteoclast physiology and potential therapeutic targets.
With the help of αvβ3 integrin the osteoclast attaches to the bone surface and forms a sealing zone. Proton pumps and chloride channels produce a highly acidic microenvironment that is essential for the catalytic activity of osteoclastic enzymes such as cathepsin K. Odanacatib inhibits cathepsin K, a lysosomal protease that degrades collagens. The tyrosine Src kinase plays a critical role in osteoclast activity and can be inhibited by saracatinib. RANKL acts as an essential regulator of osteoclast differentiation and activity. The fully human monoclonal antibody denosumab prevents RANKL binding to its receptor RANK. Abbreviations used: FAK, focal adhesion kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, RANK, receptor activator of NF-κB; RANKL, RANK ligand; TRAF-6, tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor-6