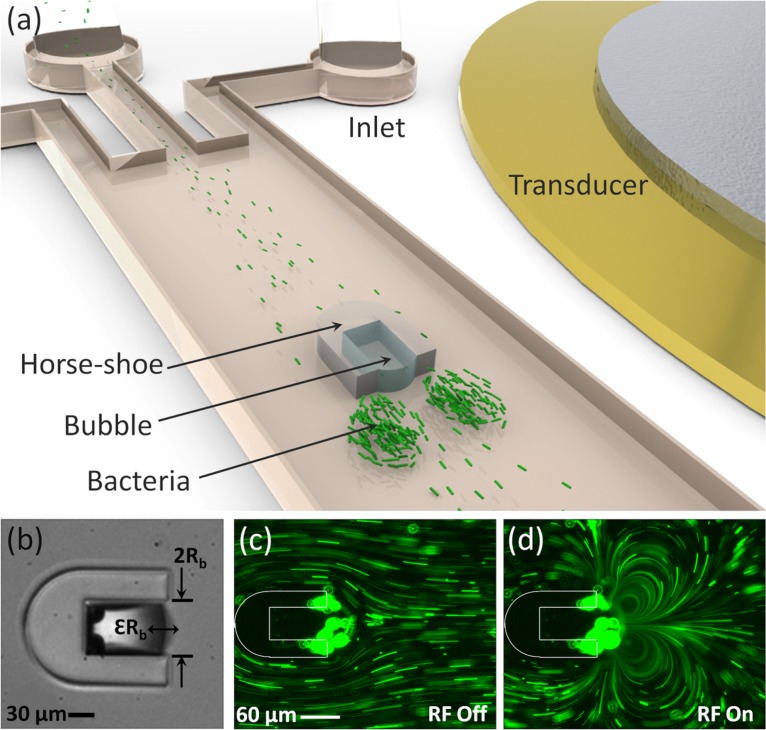
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of the microfluidic device with a built-in horseshoe structure. Bacterial suspension is injected from the inlets and collects in a pair of vortices induced by the oscillating microbubble trapped in the horseshoe. (b) The microbubble trapped in a horseshoe structure undergoes weakly linear oscillations. is the amplitude of oscillation of a bubble with diameter. A pair of vortices is generated upon applying the radio frequency signal. 1.9 μm polystyrene microbeads are used as flow tracers to demonstrate the flow field when the transducer is (c) off and (d) on. Structure of the horseshoe is shown with white lines for visualization.