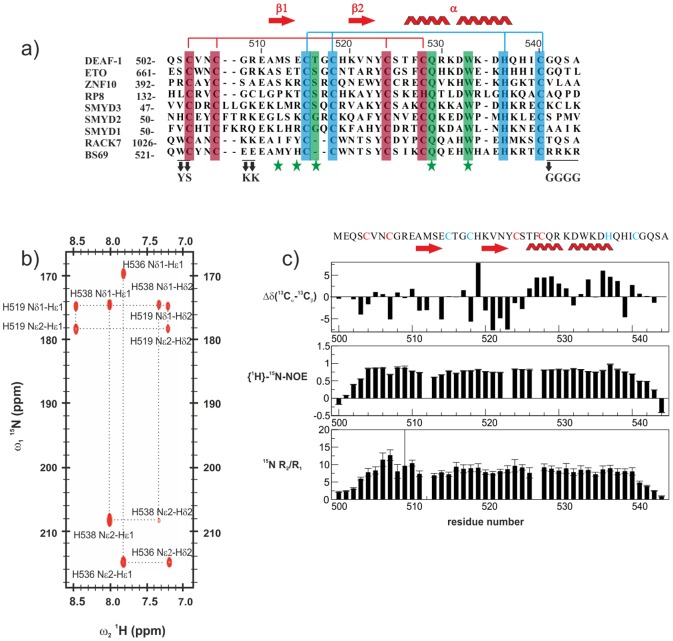
Figure 1. Primary sequence and NMR analysis of the DEAF-1 MYND domain.
(a) Sequence alignment of different MYND domains. Residues coordinating the first and second zinc ions are highlighted with red and blue background, respectively. Residues involved in binding to corepressor peptides are indicated with a green star at the bottom, and those interacting through their side chains are highlighted in green. The positions of mutations performed on BS69 are indicated at the bottom. (b) Long range 1H, 15N HSQC spectrum correlating Hε1 and Hδ2 to Nδ1 and Nε2 through 2 J HN and 3 J HN couplings (Pelton et al 1993). The spectrum reveals a different protonation pattern for each histidine sidechain corresponding to the three possible tautomeric states. (c) 13C secondary chemical shifts (top), {1H}-15N heteronuclear NOE (middle), and 15N R2/R1 relaxation rates ratio (bottom) are plotted versus DEAF-1 MYND residue numbers. The secondary structure elements and the amino acid sequence of the protein are indicated at the top of the figure. Residues coordinating the first and second zinc are colored red and blue respectively.