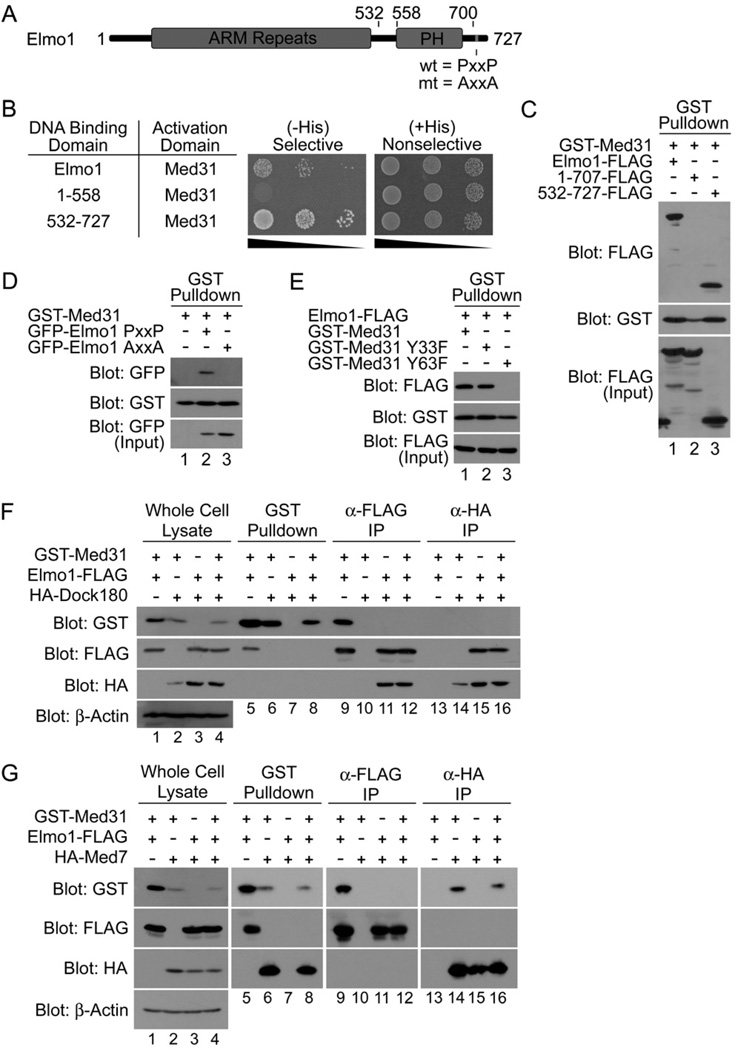
Figure 1. The engulfment protein Elmo1 interacts with the Mediator complex subunit Med31.
A. Schematic representation of Elmo1 protein. C-terminal PxxP (wild type) and AxxA (mutant) motifs are indicated. PH – pleckstrin homology. B. In a yeast two-hybrid assay, Med31 interacts with full length Elmo1 and the C-terminal PxxP-containing fragment of Elmo1 (532–727), but not with a PxxP-deletion mutant of Elmo1 (1–558), as determined by growth on selective (His-Leu-Trp-) and nonselective (His+Leu-Trp-) media at ten-fold serial dilutions. C. The C-terminal PxxP motif of Elmo1 is required for the interaction with Med31. The interaction in mammalian cells between GST-Med31 and Elmo1-FLAG, or the Elmo1 fragments, were analyzed by transiently expressing the indicated proteins in 293T cells, and analysis by precipitations and immunoblotting as shown. D. Mutation of the Elmo1 PxxP motif to AxxA abolishes the interaction with Med31. E. Med31 residue Y63 is required for binding to Elmo1. F. Med31:Elmo1 and Elmo1:Dock180 complexes are distinct. Epitope-tagged Med31, Elmo1 and Dock180 were transiently expressed as indicated, precipitated via epitope-tag, and immunoblotted as shown. G. Elmo1 is not part of the Med31:Med7 subcomplex. Indicated proteins were expressed and their association was determined by precipitation with the indicated tags and immunoblotting.