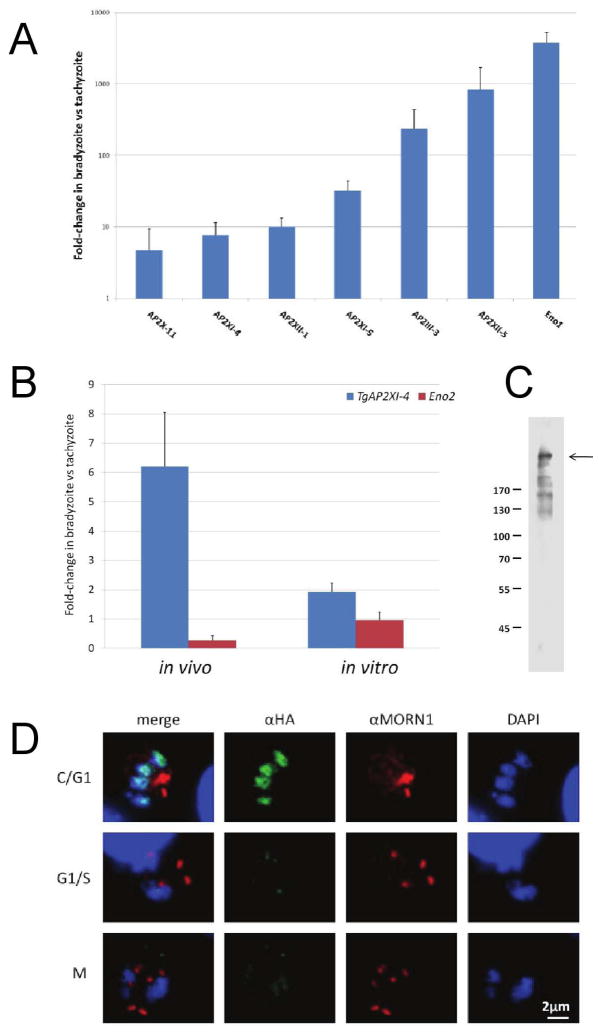
Figure 1. TgAP2XI-4 expression is regulated during bradyzoite differentiation and throughout the tachyzoite cell-cycle.
(A) Wild type parasites from a T. gondii type II 76K strain were either used to produce bradyzoite tissue cysts (in vivo) or were cultured under normal conditions for tachyzoite growth (in vitro) (Dzierszinski et al., 2001). Total RNA was purified from all samples and analysed by quantitative RT-PCR to determine the relative levels of TgAP2 genes and Eno1 mRNA. The values are presented as the fold-changes in the bradyzoite samples relative to the corresponding tachyzoite samples.
(B) Wild type parasites from a T. gondii type II strain were used to produce bradyzoite tissue cysts (in vivo) while wild type parasites from a type I strain were cultured under alkaline (pH 8.2) stress (in vitro) to induce the expression of bradyzoite genes. For comparison, type I and type II tachyzoite strains were grown in vitro under control conditions (pH 7.0). Total RNA was purified from all samples and analysed by quantitative RT-PCR to determine the relative levels of TgAP2XI-4 and Eno2 mRNA. The values are presented as the fold-change in the bradyzoite samples relative to the corresponding tachyzoite samples.
(C) A whole-cell protein lysate from the TgAP2XI-4-HA mutant was fractionated on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel under reducing conditions. Western blot was carried out using a mouse monoclonal αHA antibody. An arrow indicates the band corresponding to TgAP2XI-4-HA. Molecular weight markers are in kDa.
(D) Immunofluorescence assays were conducted on TgAP2XI-4 parasites fixed 24-hours after infection of HFF cells. The mouse monoclonal αHA antibody was used in combination with a rabbit αMORN1 antibody and detected with anti-mouse Alexa488 (green) and anti-rabbit Alexa594 (red), respectively. Daughter cell formation and mitosis were effectively monitored with αMORN1 and DAPI counterstaining (blue), respectively. TgAP2XI-4 protein expression peaks during the cytokinesis and early G1 phase. C, cytokinesis; G1, gap phase; S, synthesis phase; and M, mitosis. It should be noted that MORN1 localizes at ring structures at the apical and posterior ends of the inner membrane complex and to the centrocone. The centrocone-associated MORN1 concentrates at a focal point during G1 or as two focal points during S/M phase and is absent during C phase.