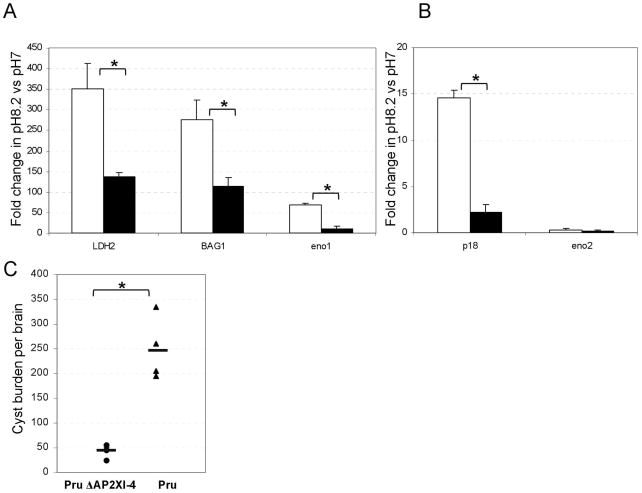
Figure 7. Phenotypic analysis of Pru ΔKu80 ΔTgAP2XI-4.
(A) Quantitative RT-PCR of bradyzoite transcripts from Pru ΔKu80 ΔTgAP2XI-4. Total RNA purified from ΔTgAP2XI-4 and parental parasites cultured under either control (pH 7) or stress (pH 8.2) conditions were analysed by quantitative RT-PCR. Genes coding for known bradyzoite proteins including LDH2, P18, BAG1 and Eno1 were analysed alongside Eno2, which is not affected by alkaline stress. Values are presented as fold-change in pH 8.2-stressed parasites relative to those in control conditions. An asterisk indicates a significant difference (P < 0.05) between the wild type and the ΔTgAP2XI-4 mutant for individual genes.
(B) Dolichos bifluorus lectin staining of parental and ΔTgAP2XI-4 strain after 2 days of treatment at pH 8.2. The percentage of vacuoles positive for lectin staining is represented. Data are means +/− SD. An asterisk indicates a significant difference (P < 0.05).
(C) Cyst burden in mouse brain. Cysts were enumerated after Dolichos bifluorus lectin staining of the cyst wall. A minimum of five mice was used per group. Brains of mice infected with the Pru ΔTgAP2XI-4 strain are represented with circles. Brains of mice infected with the Pru strain are represented with triangles. The mean cyst burden for each group is represented by a horizontal bar.