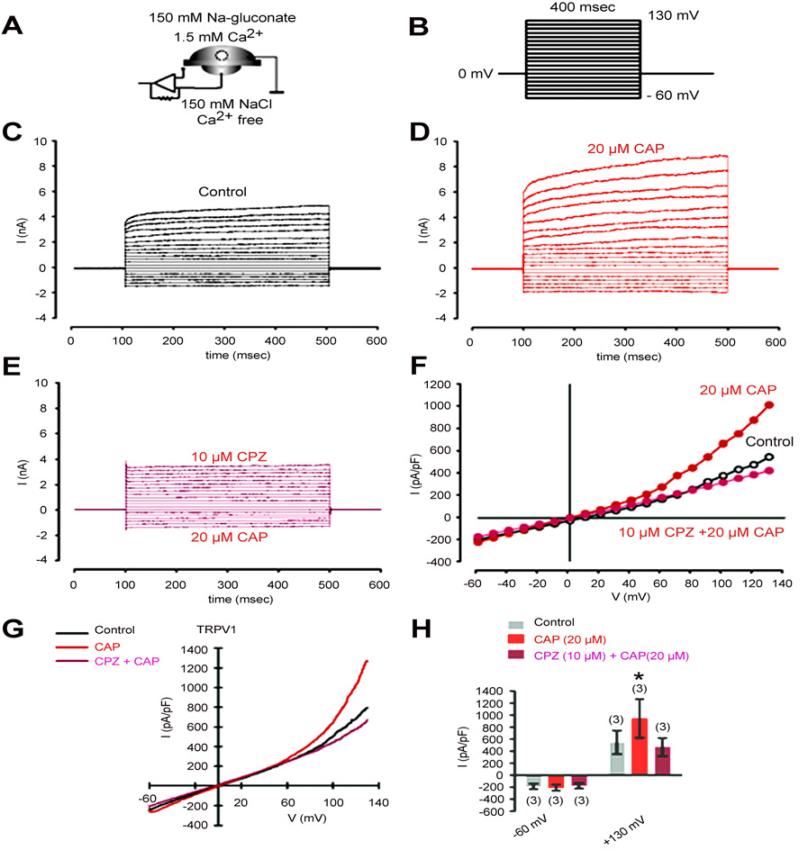
Figure 3.
CAP induces through TRPV1 activation non-selective cation channel currents in HCF. (A) Experimental design (whole-cell configuration of the planar-patch clamp technique). Currents were identified by their dependence on the permeating ion. Chloride was replaced by isosmotic gluconate substitution in the external solution to avoid chloride outward currents. (B) Voltage pulse protocol. Holding potential (HP) was set to 0 mV to avoid any voltage-dependent ion channel currents. (C) Nonselective cation channel currents induced by depolarization from -60 mV to 130 mV after establishing the whole-cell configuration (without leak current subtraction) (control). (D) Increased cation channel currents in the presence of CAP (20 μM). (E) Inhibition of CAP-induced cation channel currents in the presence of CPZ (10 μM). (F) Effects of CAP and CPZ are summarized in a current/voltage plot (I-V plot). All values are reported as means ± SEM. Data were obtained from the recordings shown in (C), (D), and (E). For the current/voltage relation, maximal peak current amplitudes were plotted against the voltage (mV). The currents were normalized to capacitance to obtain current density (pA/pF). The upper trace (red filled circles) was obtained in the presence of 20 μM CAP and the lower trace (open circles) without CAP. CAP-induced increases in non-selective cation channel outward currents at potentials above +60 mV were discernible. The second lower trace (mauve filled circles) was obtained after CPZ pre-incubation. (G) Original traces of CAP activated TRPV1 channel responses to voltage ramps from -60 mV up to +130 mV (without leak current subtraction) in the whole-cell configuration of the planar patch-clamp technique. Currents are shown before application (black), during application of CAP (20 μM, red) and after application of CPZ (mauve). The currents were normalized to capacitance to obtain current density (pA/pF). (H) Summary of the experiments with CAP in the presence of Na-gluconate in the external solution. All values are reported as means ± SEM. The asterisks (*) indicate statistically significant increases of outward currents with and without CAP (n = 3; p < 0.05; paired tested).