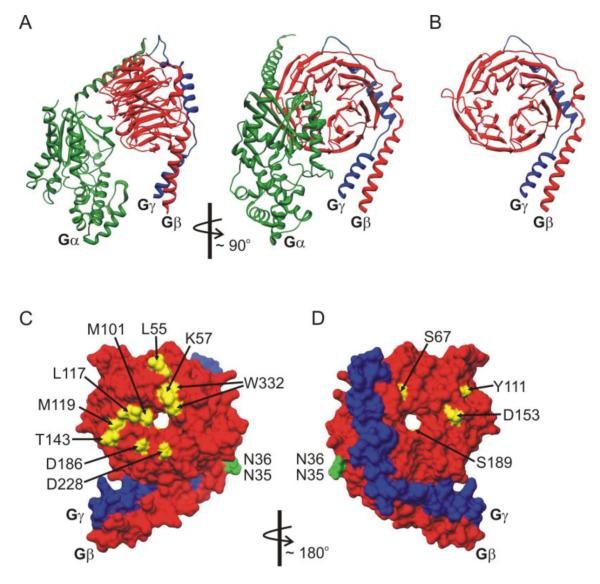
Figure 3.
Structural determinants on Gβγ that govern modulation of CaV2 channels. (A, B) Ribbon diagram renderings of the heterotrimeric G protein structure in panel A, and the Gβγ dimer in panel B (Gαi - green; Gβ1 - red; and Gγ2 blue). Gβ adopts a seven blade β-propeller structure with an α-helical N-terminal domain that binds to the α-helical N-terminus of Gγ. Gα interacts with multiple residues on the top face of Gβ and the side aspect of propeller blade 1. Many effectors bind to a protein interaction “hot spot” on the surface of Gβ that is masked by Gα in the heterotrimer. (C, D) Molecular surface rendering of the Gβγ dimer (Gβ - red; Gγ - blue). Panel C shows the Gα interacting face of Gβγ, and panel D is rotated ~180° to show opposite face of Gβγ. Residues marked in yellow have been reported to disrupt inhibition of CaV2 channels. Residues marked in green are involved in crosstalk between Gβ1 and PKC phosphorylation of CaV2.2. Molecular graphics images based on data reported by Wall et al [144] (PDB ID: 1GP2) were produced using the UCSF Chimera package [256, 257] from the Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics at the University of California, San Francisco.