Figure 2.
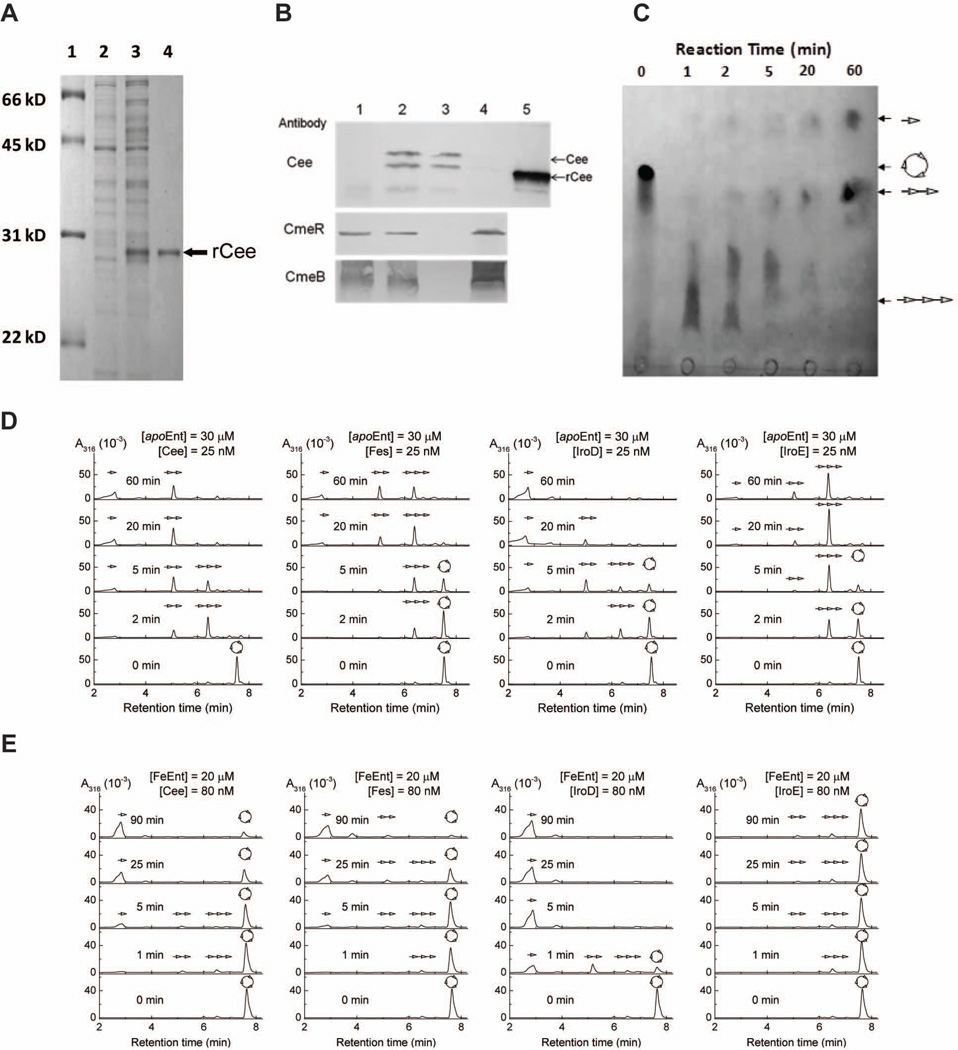
Cee is an enterobactin esterase located in periplasm of C. jejuni. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of rCee production and purification. Lane 1, molecular weight marker (Bio-Rad); lane 2, whole cell lysate of noninduced E. coli; lane 3, whole-cell lysate of E. coli induced for 3h with 1 mM IPTG; lane 4, purified rCee purified. (B) Localization of Cee. The proteins samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting analysis using CmeR as a cytoplasmic protein control and CmeB as an inner membrane control. Lane 1, whole cell lysate of C. jejuni 81–176 containing control vector pRY111 (JL229); lane 2, whole cell lysate of the C. jejuni 81–176 containing a vector that overproduces Cee (JL870); lane 3, periplasmic fraction of JL870; lane 4, spheroplastic fraction of JL870; and lane 5, the purified rCee. (C) Thin layer chromatography (TLC) analysis of the hydrolysis of Ent by rCee. The reaction time was indicated above the picture.  , Ent, or cyclic trimer of DHBS;
, Ent, or cyclic trimer of DHBS;  , linear trimer of DHBS;
, linear trimer of DHBS;  , dimer of DHBS;
, dimer of DHBS;  , DHBS monomer. (D) HPLC analysis of hydrolysis of apo Ent by Cee, Fes, IroD, and IroE. (E) HPLC analysis of hydrolysis of FeEnt by Cee, Fes, IroD, and IroE.
, DHBS monomer. (D) HPLC analysis of hydrolysis of apo Ent by Cee, Fes, IroD, and IroE. (E) HPLC analysis of hydrolysis of FeEnt by Cee, Fes, IroD, and IroE.