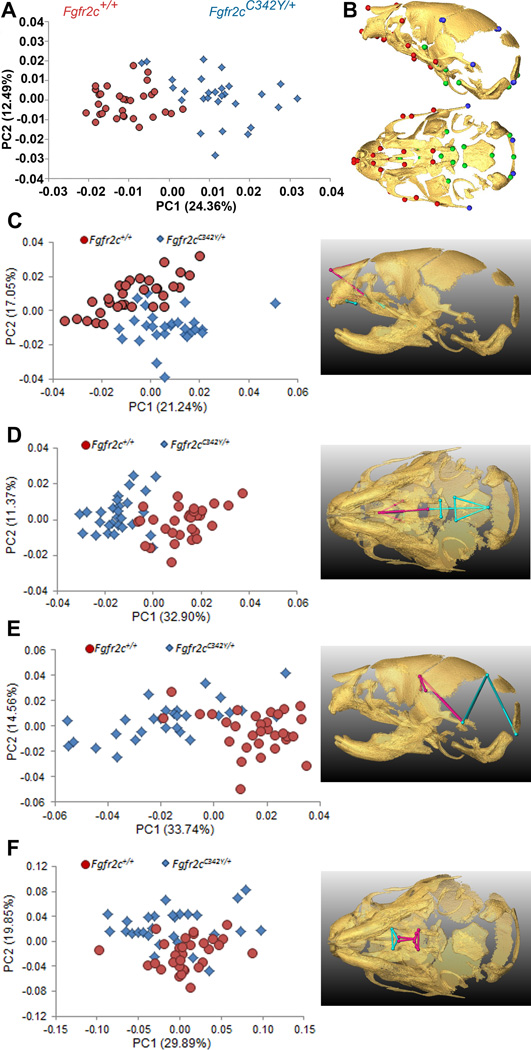
Figure 1.
Combined results of PCA of skull based on Procrustes coordinates and of EDMA of landmark coordinates. A) Scatter plots of individual scores based on PCA from global skull morphology of Fgfr2cC342Y/+ mutant mice and unaffected littermates along first and second Principal Components axes (PC1 and PC2). B) Lateral (top) and inferior (bottom) views of 3D isosurfaces of µCT reconstruction of unaffected P0 mouse skull with mandible removed displaying the 39 landmarks used in global skull shape analysis. Facial landmarks are shown in red, cranial base landmarks in green, cranial vault landmarks in blue. C-F) Results of PCA analyses based on Procrustes coordinates of regional configurations of skull landmarks on left and EDMA analysis of regional configuration of points on right. Scatter plots of individual morphologies of the facial skeleton (C), cranial base (D), cranial vault (E) and palate (F) along first two principal axes (PC1 and PC2). Since size-related differences in shape (allometry) were significant (P ≤0.05) in the analysis of the face and palate, Figs 1C and 1F represent shape variation after mathematically adjusting for correlations among shape variables due to allometric effects following (Drake and Klingenberg, 2008). Allometry did not have a significant effect on cranial base or cranial vault. EDMA results show linear distances within each regional configuration of points that show at least a 5% difference in length and are significantly different between groups by confidence intervals. Blue lines are significantly larger in mutant mice relative to unaffected littermates; fuchsia lines are significantly smaller in mutant mice.