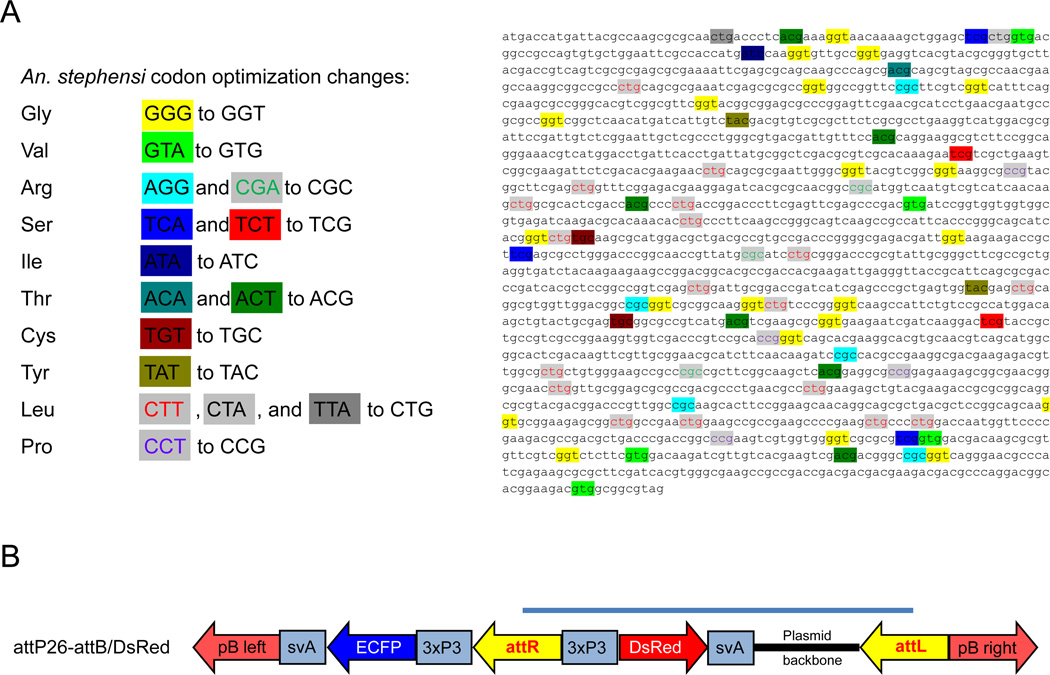
Figure 4.
Codon optimization of the ΦC31 integrase and ΦC31-mediated recombination of line attP26 with the attB/DsRed2 donor plasmid. (A). Codon optimization was performed on the DNA sequence of ΦC31 integrase P3 mutant (Keravala et al., 2009), which contained an additional 33 amino acid sequence upstream of the ‘wild-type’ ΦC31 start codon. The DNA sequence of the P3 mutant was codon optimized according to the most frequent codon usage in the An. stephensi genome, which is similar to that of Ae. aegypti. (B). Diagram of the attB/DsRed2 donor plasmid integration into the genome of docking strain attP26 following recombination between attB and attP in presence of ΦC31(‘wild-type’) or codon optimized ΦC31 P3 mutant integrases, respectively. As a consequence of recombination, attP and attB sites are converted into attL and attR. Grey bar indicates the part of the transgene that originates from the donor plasmid.