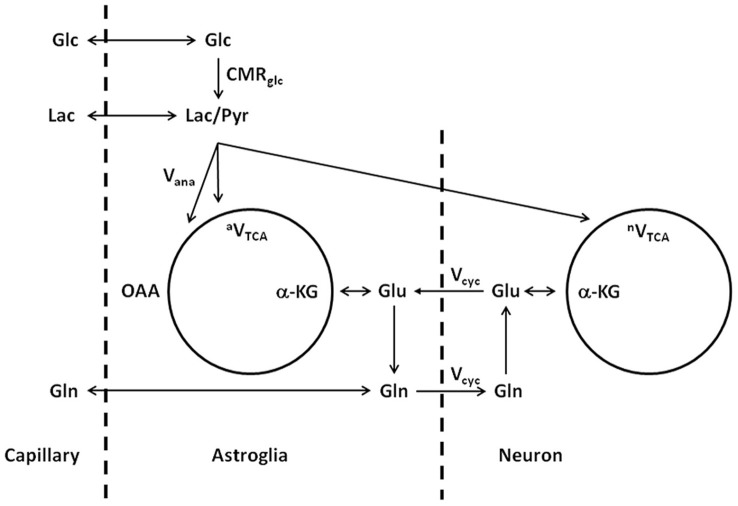
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the glutamate–glutamine cycle between neurons and astroglia and glucose metabolism (adapted from Shen et al., 1999). Released neurotransmitter glutamate is transported from the synaptic cleft by surrounding astroglial end processes. In astroglia, glutamate is converted into glutamine by glutamine synthetase. Glutamine is then released by the astroglia, transported into the neurons, and converted back into glutamate by glutaminase, which completes the cycle. Glc, glucose; Pyr/Lac, pyruvate/lactate; OAA, oxaloacetate; α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; Glu, glutamate; Gln, glutamine; CMRglc, cerebral metabolic rate of glucose utilization; Vana, anaplerotic flux for de novo synthesis of oxaloacetate; aVTCA, astroglial tricarboxylic acid cycle flux; Vcyc, glutamate–glutamine cycling flux; nVTCA, neuronal tricarboxylic acid cycle flux.