Fig. 5.
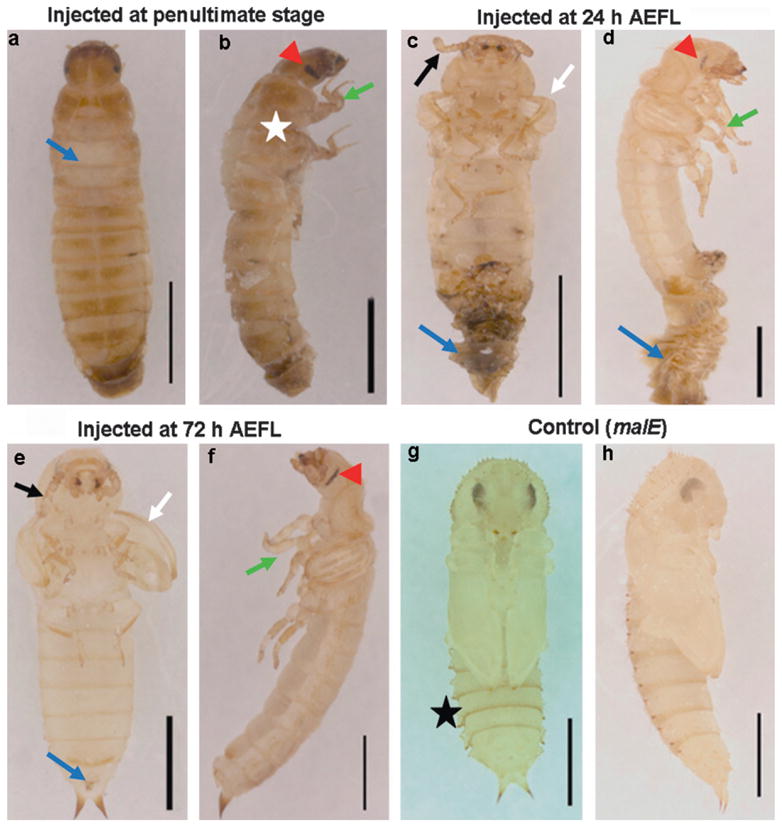
Phenotypes of knock-down of Tcbr. Tcbr or malE dsRNA (control) was injected into penultimate larval stage (a and b) or at 24 h (c and d) or at 72 h (e and f) after ecdysis into the final instar larval stage and the corresponding phenotypes are shown in comparison with control (g and h)). (a) The dorsal view, (c, e and g) the ventral view and (b, d, f and h) the lateral view of Tcbr RNAi and malE RNAi (control) insects. Injections were given within 24 h of penultimate larval stage and 24 and 72 h of last instar larval stage. (a) Split in the dorsal thoracic region (blue arrow). (b) Wing pads (white star), compound eyes (red arrow-head) and differentiated legs (green arrow). (c and d) The exuviae remained attached to the body (blue arrow) when injections are done at 24 h AEFL. Irrespective of time of injection, note the development of antennae (c and e, black arrows), wings (c and e, white arrows), legs (d and f, green arrow) and compound eyes (d and f, red arrowhead) at different differentiating states. Note the absence of gin-traps in Tcbr dsRNA injected insects (c and e) but present in the control pupal abdomen (g, black star). Scale bar: 1 mm.
