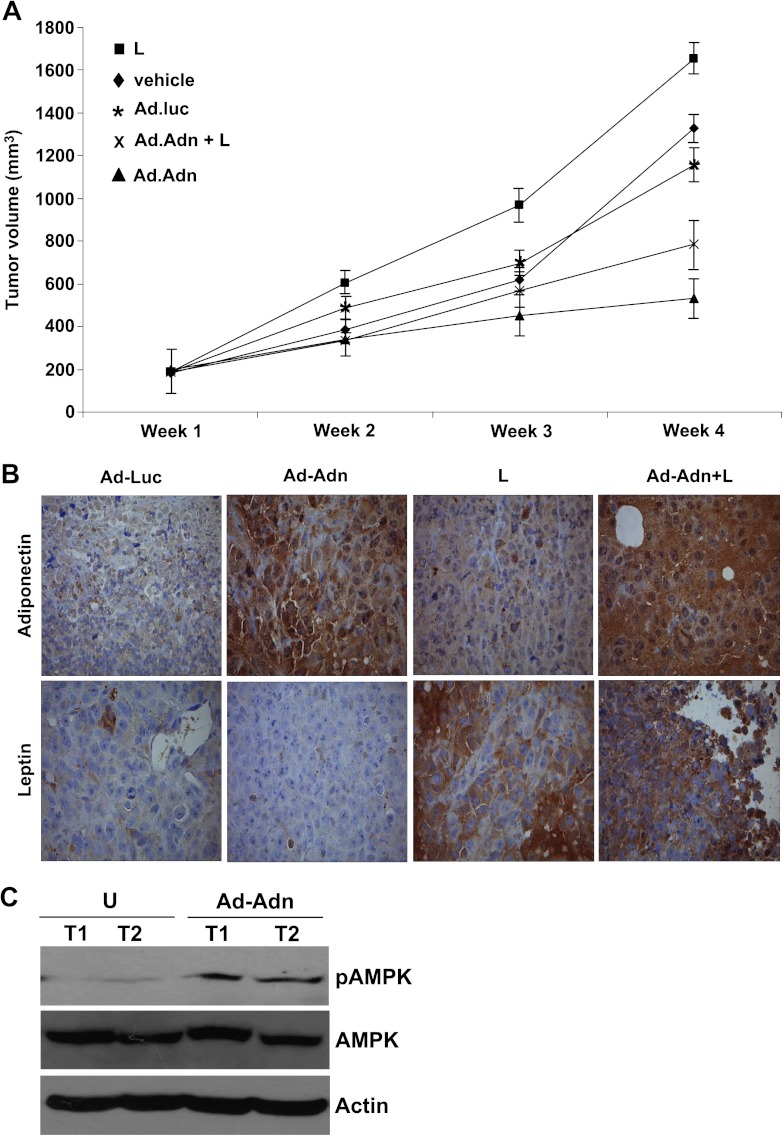
Figure 6.
Adiponectin treatment inhibits leptin-induced breast tumor growth in nude mice. MDA-MB-231 cell-derived tumors were developed in nude mice and treated with leptin (L), vehicle (V), control-adenoviral (Ad-Luc), adiponectin-adenoviral (Ad-Adn; 108 pfu), and L + Ad-Adn. (A) Tumor growth was monitored by measuring the tumor volume for 6 weeks (n = 8 mice per group). Ad-Adn treatment reduced tumor size as compared to Ad-Luc, *P < .01. Adiponectin treatment significantly reduced leptin-induced tumor size as compared to leptin alone (P < .01) and Ad-luc (P < .01). (B) Tumor samples were subjected to immunohistochemical analysis using leptin and adiponectin antibody. Ad-Adn-treated tumors showed significant increase in adiponectin expression as compared to Ad-Luc-treated tumors, *P < .05 Ad-Adn versus Ad-Luc. Leptin-treated tumors showed significant increase in leptin expression as compared to Ad-luc, *P < .05 leptin versus Ad-Adn. (C) Tumor lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using pAMPK, AMPK, and actin antibodies. Adiponectin-treated tumors showed increased phosphorylation of AMPK showing increased adiponectin signaling.