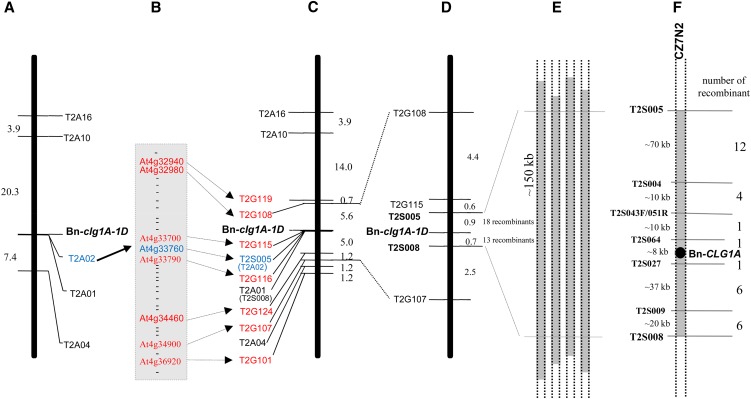
Figure 2.
Mapping and Positional Cloning of Bn-CLG1A.
(A) Initial mapping of five AFLP markers on a population of 255 segregant DH lines derived from a cross between B001-Clg and cv Yudal. The genetic distance (centimorgans) between markers is shown on the left.
(B) Thirty-two Arabidopsis genes from a region of 2030 kb of chromosome IV around the At4g33760 gene were used for generation of additional PCR markers.
(C) Seven genes (in addition to At4g33760 gene) produced polymorphic PCR markers and were mapped around Bn-clg1A-1D on the same 255 DH segregating population.
(D) Finer genetic mapping of Bn-clg1A-1D on a larger DH population of 2158 lines.
(E) Identification of four BAC clones from Darmor-bzh BAC library, containing the closest flanking genetic markers: T2S005 and T2S008 and Bn-CLG1A.
(F) The BAC clone CZ7N2 was sequenced (237,660 bp) and shows that T2S005 and T2S008 delimit a region of 150 kb, whose sequence were used to generate five additional PCR markers. These were used to precisely locate Bn-CLG1A, using the 31 lines that show recombination between T2S005 and T2S008, to an ∼8-kb interval containing a single candidate gene, encoding a putative RINGv E3 ubiquitin ligase.