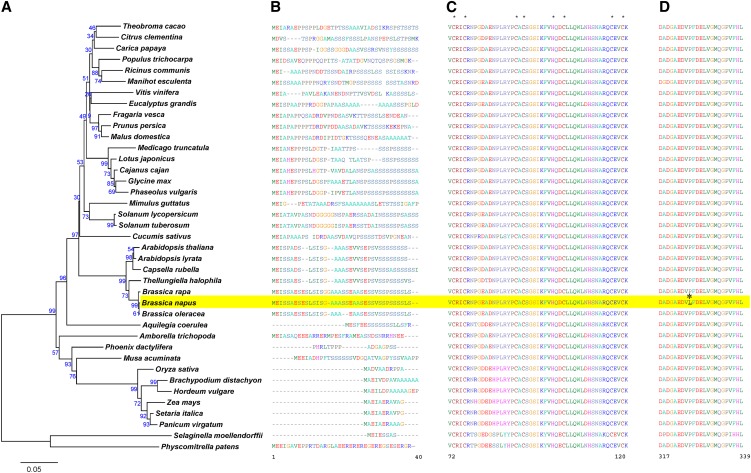
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic analysis of plant homologs of Bn-CLG1A and amino acid sequence alignment of important domains.
Phylogenetic analysis was done with homologs of Bn-CLG1A from 39 plant species. (A). The chloroplastic domain characterized by enrichment of the Ser amino acid (B). The RINGv domain characterized by conserved eight metal ligands marked with an asterisk (C). The highly conserved cleistogamy domain where the cleistogamy mutation P325L (asterisk) occurred in the B. napus Bn-clg1A-1D allele (D). Amino acid sequences were aligned using ClustalX (Thompson et al., 1997). The phylogeny analysis was performed with MEGA version 4.1 using the neighbor-joining method (Tamura et al., 2007). The percentage of replicates in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) is shown next to the branches. Amino acid numbering is presented according to the Bn-clg1A-1D sequences of B. napus (highlighted in yellow). (See Supplemental Data Set 1 online for sequence alignment.)