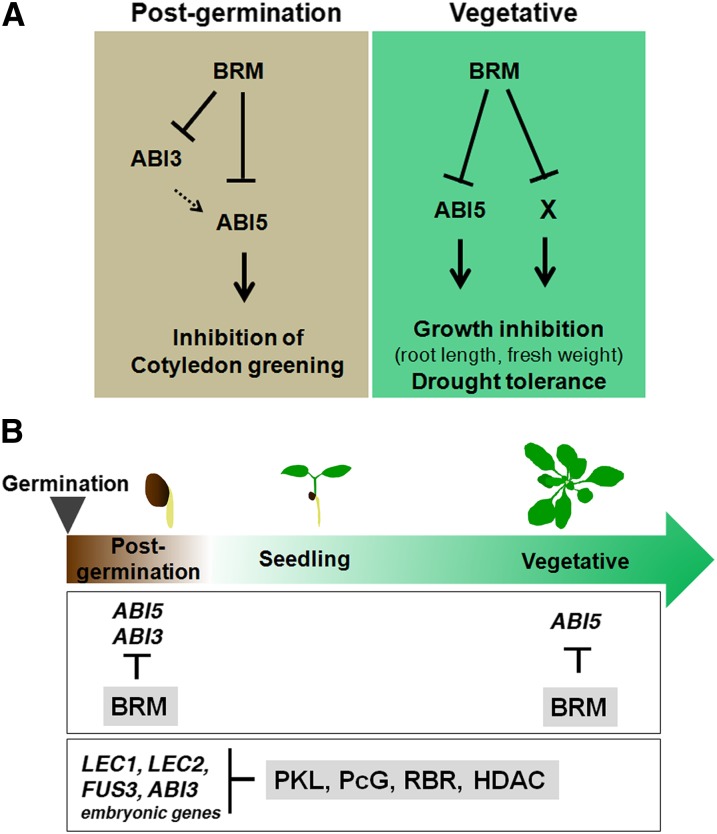
Figure 8.
Model for Role of BRM in ABA Responses.
(A) Role of BRM in ABA response at different developmental stages. Left: Inhibition of cotyledon greening during postgermination development. BRM negatively regulates the expression of two key ABA-related transcription factors ABI5 and ABI3. ABI3 acts upstream of ABI5 (Lopez-Molina et al., 2002). Solid arrows, direct regulation; dashed arrows, direct or indirect regulation. Right: Inhibition of growth during vegetative development. Additional direct BRM targets remain unidentified that act in parallel with ABI5. ABI5 has been implicated in drought tolerance (Lopez-Molina et al., 2001), although the increase of ABI5 expression alone was not responsible for the brm mutant drought tolerance.
(B) Role of chromatin regulators in expression of ABA-responsive transcription factors during postgermination and vegetative development. BRM represses ABI5 expression during postgermination and vegetative development and ABI3 during postgermination development. Several chromatin regulators influence the developmental transition from postgermination development to seedling establishment. HDAC, histone deacetylase; PcG, Polycomb; RBR, Retinoblastoma-related protein.