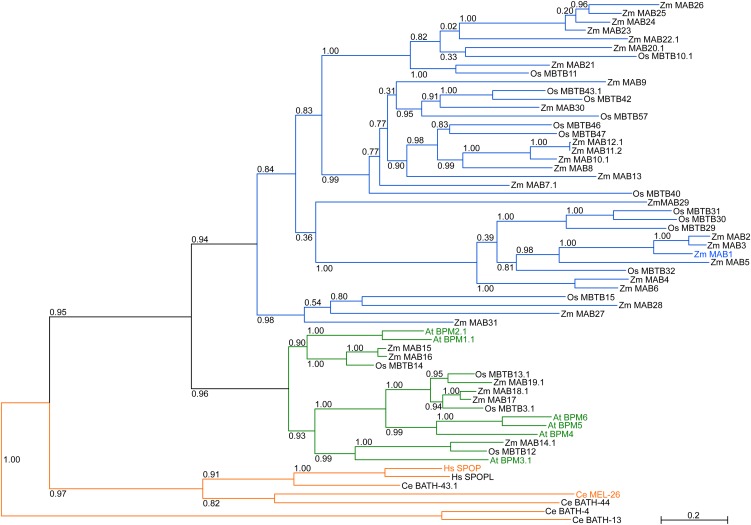
Figure 1.
The Phylogenetic Tree of Maize, Rice, Arabidopsis, Human, and C. elegans MATH-BTB Homologs.
Entire protein sequences of 31 identified maize, six Arabidopsis, 17 selected rice, two human, and five selected nematode MATH-BTB genes were analyzed. Plant MATH-BTB proteins separate into two major groups classified by Gingerich et al. (2007) as core and expanded groups. The animal group forms its own clade. Individual members of the plant core group are represented by green branches; Arabidopsis MATH-BTB proteins are highlighted in green. The expanded group containing only grass proteins is indicated in blue and the most studied members are highlighted in orange. Zm MAB1 is highlighted in blue. The numbers on each node are the Shimodaira-Hasegawa–like test indices of statistical support provided by PhyML. Bar = 0.2 is a branch length that represents nucleotide substitutions per site. For sequence identifiers, see Supplemental Table 1 online.