Table 1.
Molecular characterization of ascospore progeny from cross Q176 × IB 08/921
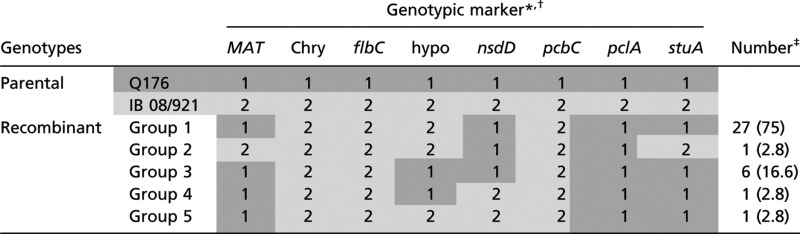 |
Progeny were classified into five recombinant groups based on 12 genotypic markers (eight shown) obtained by Southern hybridization or RFLP analysis (see Fig. 1C and Fig. S1). Numerical values (1 and 2) indicate whether the gene was derived from the MAT1-1 (dark gray shading) or the MAT1-2 (light gray shading) parent, respectively. Gene abbreviations and products: Chry, putative chrysogenin synthase; flbC, C2H2 conidiation transcription factor; hypo, hypothetical gene (Pc24g01940); nsdD, GATA-type sexual development transcription factor; pcbC, isopenicillin N synthase; pclA, phenylacetyl-CoA ligase; stuA, helix–loop–helix transcription factor.
*The following genes failed to identify additional recombinant phenotypes, most probably due to linkage with other marker genes (see Fig. S1B): flbB, bZIP transcription factor; fluG, developmental activator; penDE, acyl-CoA:isopenicillin N acyltransferase; UDP, UDP-glucose 4-epimerase like.
‡Number of progeny per group; number in parentheses indicates the percentage.
