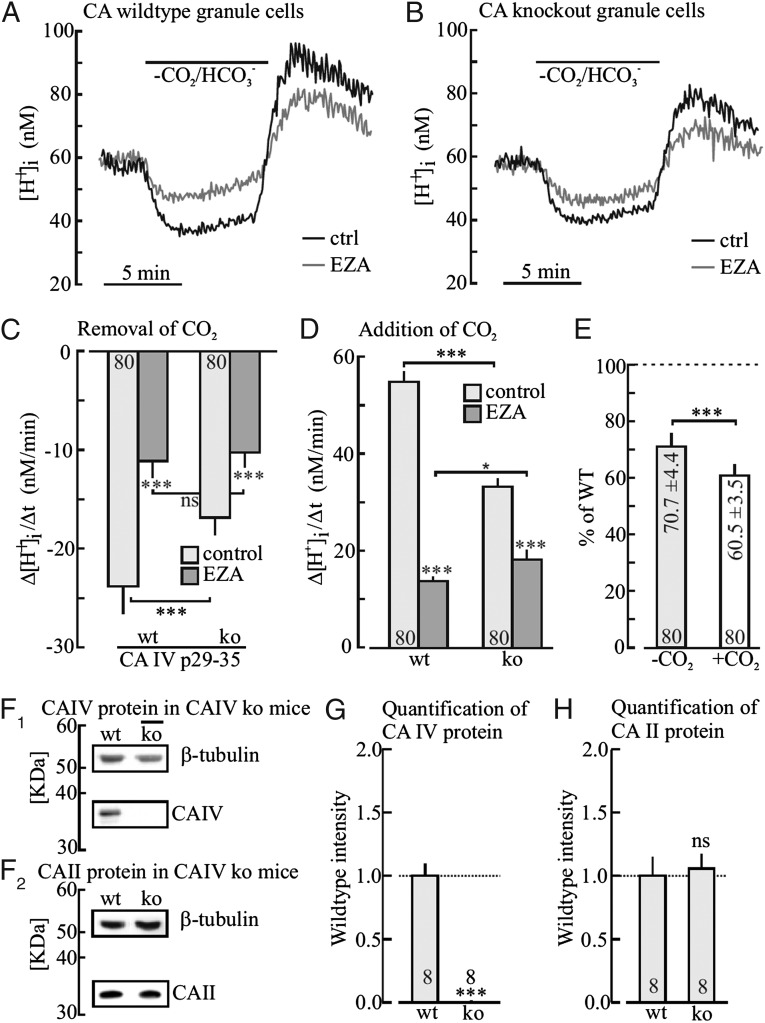
Fig. 4.
Cytosolic H+ shifts in cerebellar granule cells following removal and addition of 5% CO2/25 mM HCO3− before and after inhibition of CA activity by ethoxyzolamide (EZA, 30 µM), as measured in BCECF-loaded acute cerebellar tissue slices of wild-type and in CA IV–deficient mice (A and B). Plot of the rate of H+ shift during removal (C) and during addition (D) of CO2 in the absence and presence of EZA and of the reduction of the rates of H+ shifts in CA IV−/− mice (E). Western blots of CA IV, β-tubulin (F1), CA II, and β-tubulin (F2) in wild-type and knock-out mice, and relative quantification of CA IV (G) and CA II (H) protein levels in CA IV−/− relative to wild-type mice.