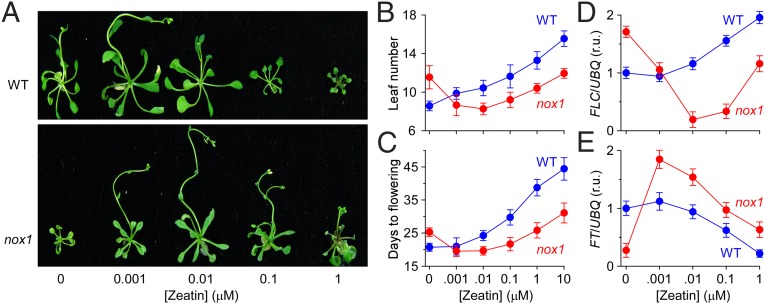
Fig. 2.
Exogenous zeatin rescues the late-flowering phenotype in nox1 resulting from elevated NO. (A) The cytokinin zeatin rescues the late-flowering phenotype in nox1. WT and nox1 seedlings were grown on MS media containing several concentrations of trans-zeatin under 16-h light/8-h dark cycles and were photographed after 25 d of growth. (B and C) Quantification of flowering time measured as the days to flowering (C) and the number of rosette leaves (B) (mean ± SD; n = 180 seedlings) from plants grown as in A. (D and E) Quantification of the FLC (D) and the FT (E) expression in response to zeatin treatments, respectively, using the methods as described in Fig. 1. Seedlings were grown on media containing several concentrations of trans-zeatin under long days for 10–12 d. The relative mRNA abundance was normalized to the UBQ levels. The relative mRNA abundance of WT at 0 μM zeatin was arbitrarily set to 1 (mean ± SEM; n = 3).