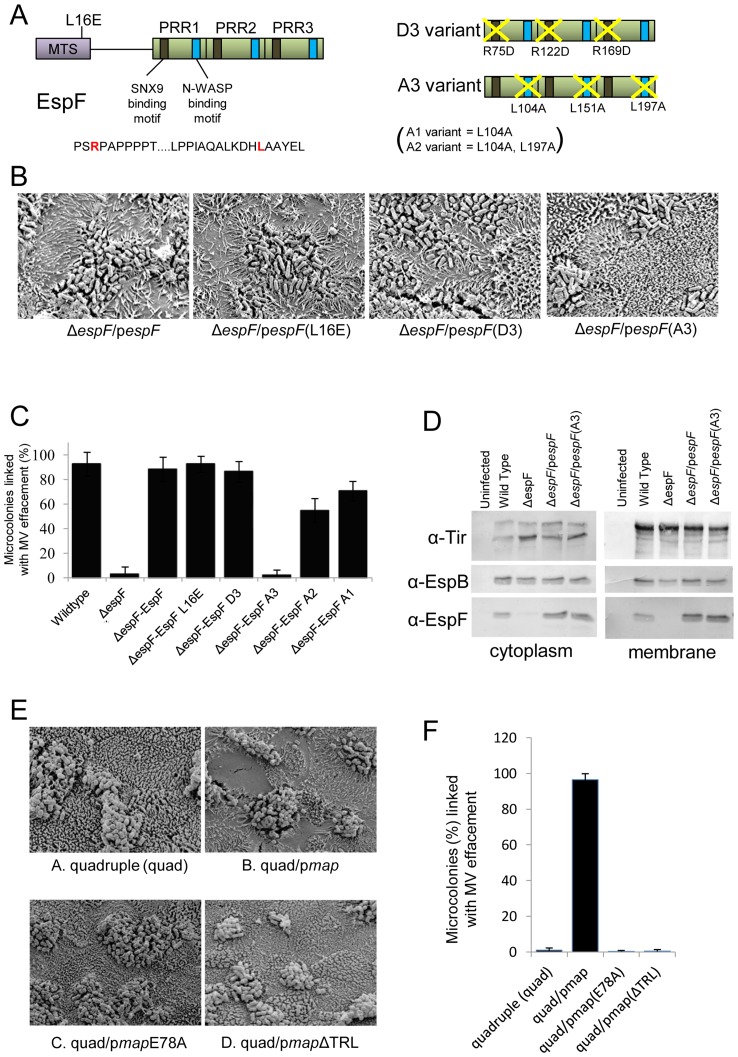
Figure 4. The EspF N-WASP binding motif is critical for effacement activity on TC-7 cells.
Schematic of the EspF protein (A) showing proline rich repeat (PRR) C-terminal domain. Represntative sequence of the sorting nexin 9 (SNX9) and N-WASP binding motifs is shown with the critical arginine and leucine shown in red in red respectively (A). The diagram on the right shows the D3 EspF variant with the arginines of all 3 SNX9 motifs substituted for aspartic acid. The A3 variant has the critical leucines in all 3 N-WASP motifs replaced with alanine. Scanning electron microscopy revealed the espF gene could functional complement the espF mutant on TC-7 cell with no role for mitochondrial targeting or the SNX9 binding motif but a crucial role for multiple N-WASP binding motifs (B). Quantification of effacement was performed by assessing percentage of microvilli removed from the apical surface from 3 separate experiments, 5 fields of view per experiment (C). Data shows mean ± SE with p values given in the text. (D) Western blot analysis using antibodies against Tir, EspF and EspB in the cytoplasmic and membrane fractions of cells infected with the indicated EPEC mutants. (E) Scanning electron micrographs of TC-7 apical surface infected with the quadruple (quad; lacking Tir, Map, EspF and Intimin) complemented with the indicated plasmids. Effacement in (F) was quantified as in (C).