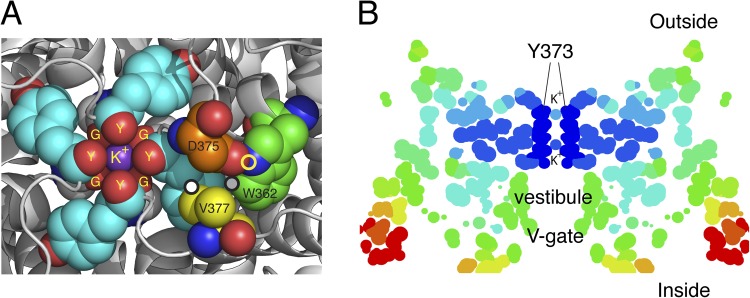
Figure 2.
Structural arrangements of the Kv1.2-2.1 chimera (2R9R) near the pore. (A) The outermost K+ ion in site 1 (S1) of the filter is tightly complexed to the four carbonyls of Y373 (Y445) (Y) and the four carbonyls of G372 (G444) (G), just below. Several residues important in C-type inactivation are labeled. The carbon atoms of these residues are rendered with different colors for clarity: gray, G372 (Y444) in ShB; cyan, Y373 (Y445); orange, D375 (D447); yellow, V377 (T449); green, W362 (W434). Y373 (Y445) and G372 (G444) from all four subunits are shown, but only one set of D375 (D447), W362 (W434), and V377 (T449) is shown as spheres. D375/447 and W362/434 residues shown are from one subunit, whereas V377 (T449) is from an adjacent subunit. The circles mark three of the close contacts postulated to be important for C-type inactivation (see text). Prepared using MacPyMol (version 0.99). (B) A “temperature” map of a section obtained from the B-factor values along the pore axis of 2R9R. Dark blue marks regions of high stability, ranging through light blue, yellow, orange, and red as stability decreases progressively away from the selectivity filter. Prepared using RasMol.