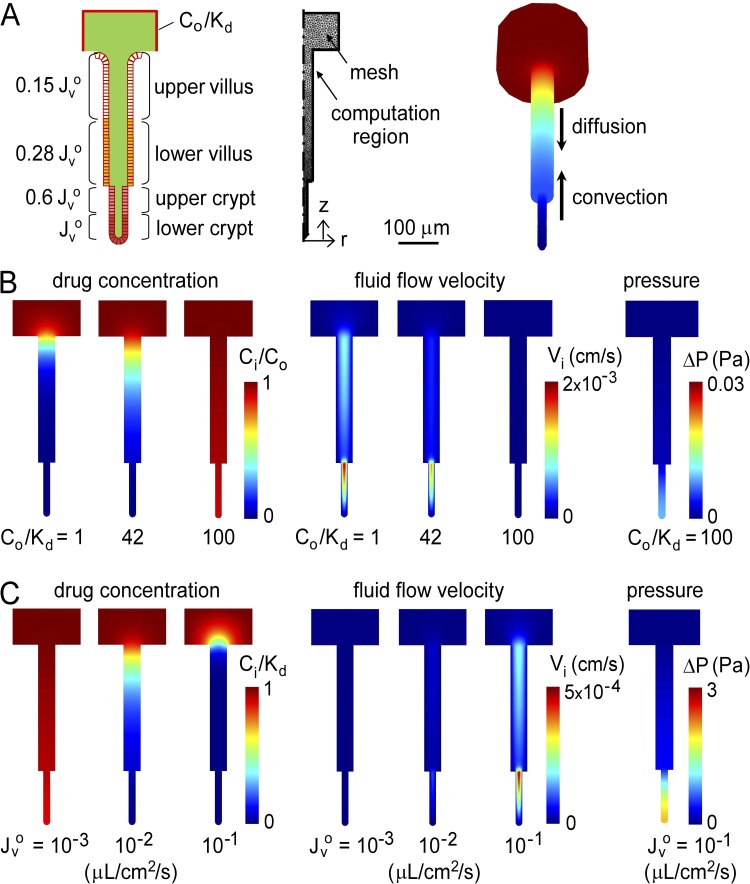
Figure 2.
Convective inhibitor washout in single crypts. Inhibitor convection–diffusion was solved for a cylindrical crypt–villus unit exposed at its outer boundary (intestinal lumen) to a constant concentration of membrane-impermeant inhibitor, Co/Kd. (A) Cross section of a cylindrical crypt–villus unit showing relative Jvo at indicated regions (left). Two-dimensional computation volume showing mesh elements (middle). Equivalent three-dimensional crypt–villus unit showing downward inhibitor diffusion and upward convection. (B) Steady-state profiles of drug concentration (left), fluid flow velocity (middle), and pressure (right) for single-crypt diffusion–convection for indicated Co/Kd, with Jvo = 4 × 10−2 µL/cm2/s. (C) Steady-state profiles for indicated Jvo, with Co/Kd = 1.