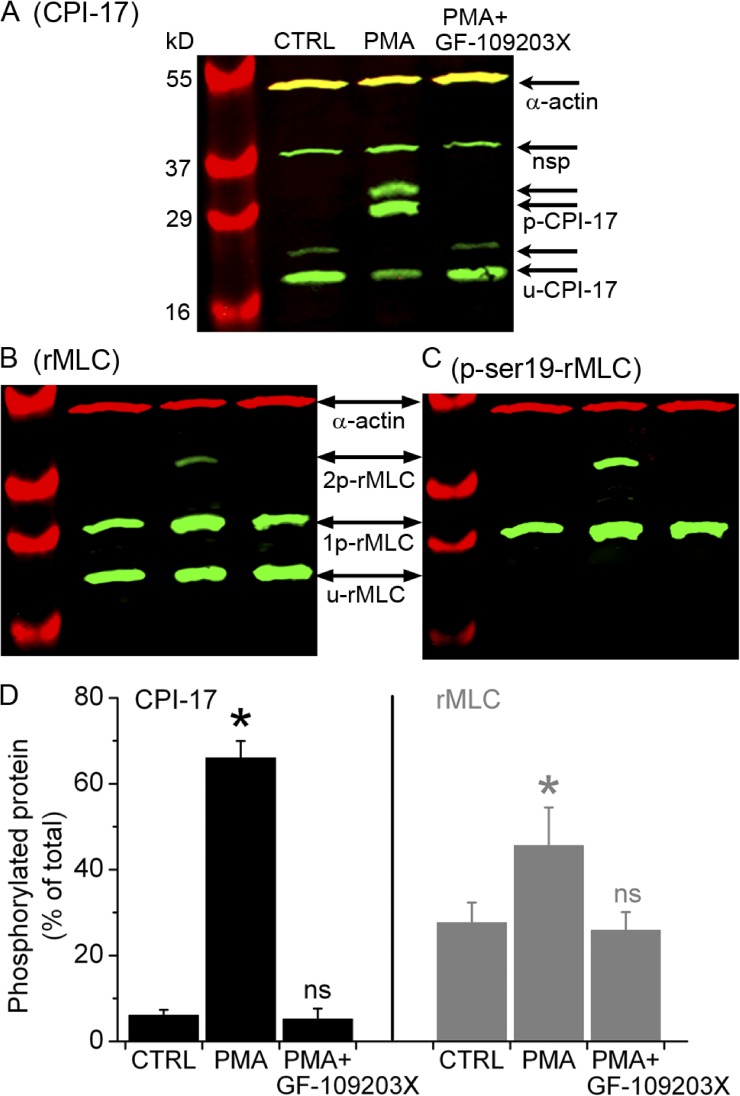
Figure 9.
Phosphorylation of CPI-17 and rMLC induced by PMA and inhibited by GF-109203X. Separation of (A) phosphorylated (p-CPI-17) and unphosphorylated (u-CPI-17) CPI-17 and (B and C) mono-phosphorylated (1p-rMLC), bi-phosphorylated (2p-rMLC), and unphosphorylated (u-rMLC) rMLC by SDS-PAGE with polyacrylamide-bound phosphate-binding tag (Phos-tag SDS-PAGE) and detected by specific antibodies using Western blot. The Western blots in B and C were obtained after stripping previous antibodies and reprobing the membrane in A with antibodies directed against total rMLC and subsequently against phosphorylated rMLC at serine 19 (p-ser19-rMLC), respectively. Samples were prepared from selected lung slices that contained airways but not arteries and were incubated with 20 mM caffeine plus 25 µM ryanodine for 5 min, washed with sHBSS, and then incubated for 40 min with sHBSS (CTRL), 10 µM PMA, or PMA followed by 10-min exposure to 1 µM GF-109203X (upper labels). The antibody against CPI-17 detected two CPI-17 splice variants (arrow pairs) along with a nonspecific (nsp) band, as indicated by the manufacturer. Parallel samples were separated in an SDS-PAGE without Phos-tag to identify the phosphorylated/unphosphorylated CPI-17 and rMLC by verifying that each of these forms migrated in the same position in the gel without Phos-tag. SMC α actin was detected in all samples. (D) Ratio values (mean ± SEM) of p-CPI-17 to total CPI-17 and 1p+2p-rMLC to total rMLC from three experiments similar to that presented in A and B from three mice are shown.