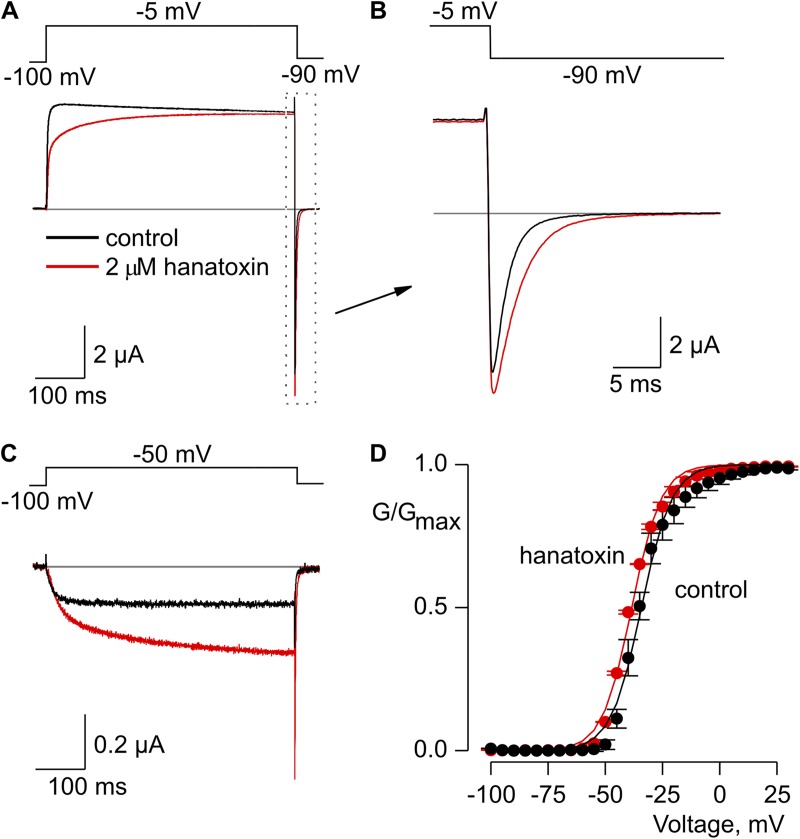
Figure 1.
Hanatoxin modified the gating of the Shaker Kv channel. (A) Voltage-activated Kv channel currents in response to strong depolarization in the absence (black) and presence (red) of 2 µM hanatoxin in the external recording solution. The gray line indicates the zero current level. (B) Expanded view of tail currents from A. (C) Voltage-activated Kv channel currents in response to weak depolarization in the absence (black) and presence (red) of 2 µM hanatoxin. (D) Normalized G-V relation in the absence (black circles) and presence (red circles) of 2 µM hanatoxin. Smooth curves are Boltzmann fits to the data with the following V1/2 and z values: −33 mV and 4 for control; −36 mV and 3.8 for toxin. Conductance was measured using tail currents and the external solution contained 50 mM Rb+. Error bars indicate SEM (n = 3).