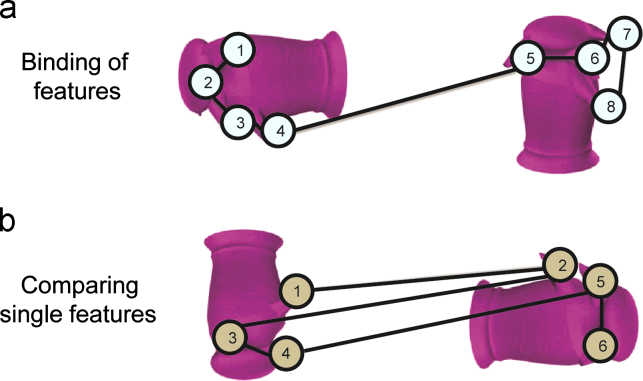
Fig. 2.
Calculating the proportion of fixations made within vs. between items. Displayed above are two possible strategies of comparing the two items (numbered circles represent fixations). For example, when comparing the two items in (a) this measure would yield: (fixations within)/(fixations between)=(3+3)/1=6. In example (b) this measure would be: (fixations within)/(fixations between)=(1+1)/(1+1+1)=0.66.