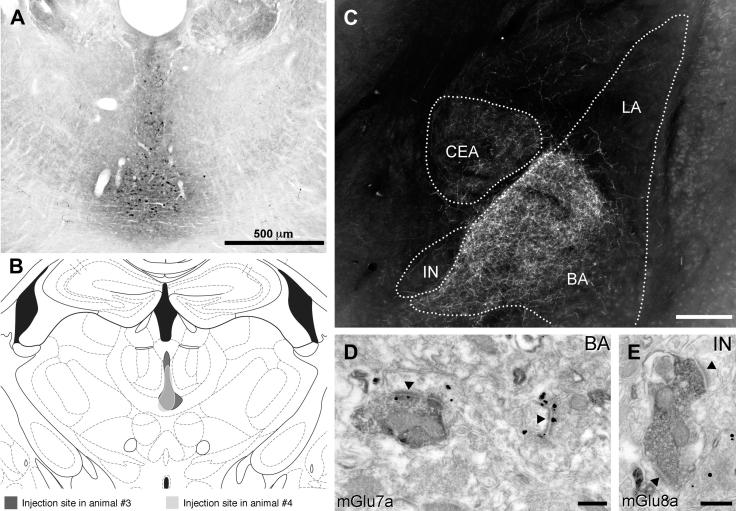
Fig. 8.
Thalamic midline efferents to the amygdala contain presynaptic mGlu7a, but not mGlu8a receptors. (A) Photomicrograph showing a PHA-L injection site in the thalamic midline nuclei (mouse #3). (B) Line drawings of a coronal section showing the extent of the PHA-L injection in the thalamus for the two selected cases. Each injection is illustrated with a different shading pattern. Both injections largely overlap and are primarily located within the paraventricular, intermediodorsal and central medial thalamic nuclei. (C) Darkfield photomicrograph showing the distribution of PHA-L-labelled fibres in the amygdala. The terminal zone appears predominantly intense in the intermediate subdivision of the BA, moderate in the lateral division of the central nucleus and a few labelled axons can be observed in the main ITC nucleus and in the intermediate capsule. (D) Electron micrograph of a PHA-L-labelled thalamic terminal (filled by a dark electron dense reaction product) immunopositive for mGlu7a receptor (immunometal particles are visible at the active zone) and forming an asymmetric synapse (indicated by an arrowhead) with a large spine of a BA neuron. Nearby another axon terminal also showing presynaptic mGlu7a receptor labelling (immunometal particles) forms an asymmetric synapse (indicated by an arrowhead) with a small spine and lacks PHA-L labelling. This spine shows immunometal particles at its plasma membrane indicative of mGlu1α receptor labelling. (F) Electron micrograph of a PHA-L-labelled thalamic axon terminal (filled by a dark electron dense reaction product) immunonegative for mGlu8a receptor and forming two asymmetric synapses (indicated by arrowheads) with dendritic spines of an ITC neuron in the IN. Abbreviations: BA, basal nucleus of the amygdala; CEA, central nucleus of the amygdala; Imp, medial paracapsular ITC cluster; IN, main ITC nucleus; LA, lateral nucleus of the amygdala. Scale bars: A, 500 μm; C, 200 μm; D, 200 nm; E, 250 nm.