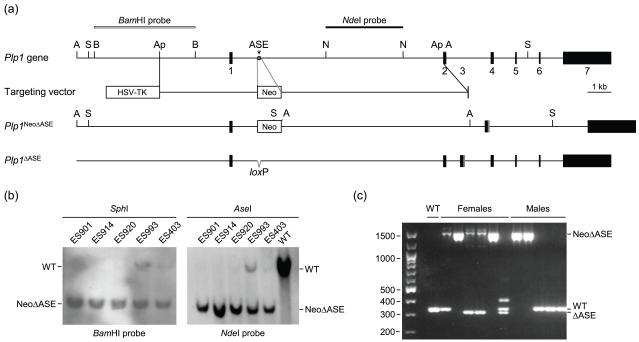
Fig. 2.
Strategy and validation for removal of the ASE from the native mouse Plp1 gene. (a) Restriction map of the mouse Plp1 gene is diagrammed at the top with only the pertinent restriction enzymes sites indicated: ApaI (Ap), AseI (A), BamHI (B), NheI (N), and SphI (S). Numbered boxes depict the seven major exons. The terminal portion of exon 3 (gray box) encodes the PLP-specific region absent from DM20. The targeting vector contains sequences encoding selectable markers for negative (HSV-TK) and positive (Neo) selection to enrich for ES cells that underwent homologous recombination. The ‘left arm’ of the targeting vector contains 3.7 kb of Plp1 DNA from the proximal ApaI site in the 5′-flanking region to intron 1 position 1083, while the ‘right arm’ encompasses sequence from intron 1 position 1177 to the ApaI site in exon 2. Thus, recombination with the targeting vector will result in deletion of the ASE (gray star) from the native Plp1 gene, with a floxed Neo gene cassette in its place (Plp1NeoΔASE). Incorporation of the Neo cassette introduces a new SphI and AseI site to the locus (only these site are indicated in the Plp1NeoΔASE allele). The Neo cassette was subsequently removed by crossing Plp1NeoΔASE mice with Cre-deleter mice (EIIa-cre C57BL/6 mice) to generate mice with the Plp1ΔASE allele, which contains a single loxP site in lieu of the ASE. (b) Validation of ES clones that underwent homologous recombination with the targeting vector by Southern blot analysis. Genomic DNA was isolated from the indicated ES clones and a wild-type (WT) control, digested with SphI or AseI, and hybridized to the BamHI and NdeI probes, respectively. All of the ES clones shown contain the Plp1NeoΔASE allele (NeoΔASE). Clones ES920, ES993 and ES403 were also positive for the native Plp1 allele (WT) to varying degrees, indicating contamination with ES cells that had not undergone homologous recombination (perhaps due to incomplete selection with G418 and/or ganciclovir). Clones ES901 and ES 914 were injected into 129/SvJ blastocysts and subsequently implanted in pseudopregnant C57BL/6 females. Resulting male chimeras (F0 founders) were bred with C57BL/6 (WT) females and the F1 progeny screened for the rearranged gene (Plp1NeoΔASE). (c) PCR genotyping of progeny resulting from a parent harboring the Plp1NeoΔASE allele. Some of the female progeny contain the EIIa-cre transgene as well. Primers used for genotyping generate amplicons of 315 (Plp1ΔASE), 333 (Plp1), and 1505 (Plp1NeoΔASE) bp. Notice that removal of the Neo cassette was incomplete in two of the females; both ΔASE and NeoΔASE products were generated. The upper band (~400 bp) in the right lane of females is a hybrid between WT and ΔASE strands.