Fig. 3.
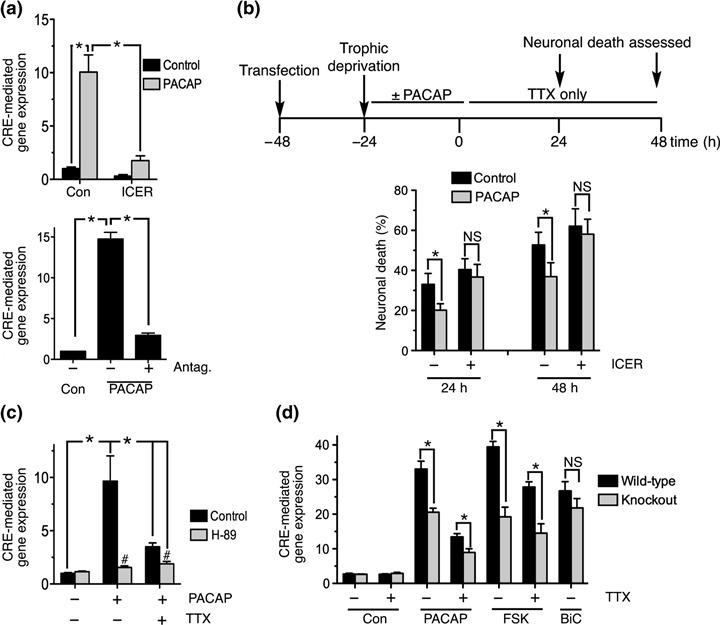
PACAP induces CRE-dependent gene expression, which is neuroprotective, and relies on AP firing. (a) Upper-PACAP induces CRE-mediated gene expression. Neurons were transfected with a CRE-Firefly luciferase vector, pTK renilla transfection control and vectors encoding either ICER1 or control (β-globin). See Methods section for exact quantities used. At 24 h post-transfection, neurons were treated with PACAP and luciferase expression was measured after a further 4 h. CRE-Firefly luciferase activity was normalised to Renilla control (*p < 0.05, n = 3). Lower-Effect of the PACAP antagonist (Antag, PACAP6–38, 1 μM) on PACAP induction of CRE-luciferase (*p < 0.05, n = 3). (b) PACAP mediated long-lasting neuroprotection depends on activation of CRE-mediated gene expression. Upper panel illustrates the experimental protocol. Briefly, neurons expressing GFP plus either ICER1 or β-globin control were treated ± PACAP 24 h post-transfection and then all cells were placed in TTX-containing medium after a further 24 h, at which point images of GFP-expressing neurons were taken (t = 0 in the upper schematic). The fate of these cells was then monitored at 24 and 48 h after this medium change. 250–400 cells were analysed per treatment across six cultures within three independent experiments. (*p < 0.05). (c) PACAP induced CRE-dependent gene expression is dependent on AP firing. Neurons were treated with PACAP where indicated for 4 h; all other drugs were added 1 h beforehand (*p < 0.05, #p < 0.05 comparing H-89 with control for that particular PACAP/TTX condition, n = 7). (d) PACAP and forskolin-induced activation of CRE-mediated gene expression is disrupted in RIIβ-deficient neurons: both AP firing-dependent and independent components. Forskolin was used at 5 μM. For comparison is an illustration of the RIIβ-independence of CRE activation triggered by promoting AP firing by network disinhibition through treatment with the GABAA receptor blocker bicuculline (50 μM) plus 250 μM 4-aminopyridine, which is a PKA-independent way of inducing AP firing (Papadia et al. 2005) (*p < 0.05, n = 6).
