Fig. 5.
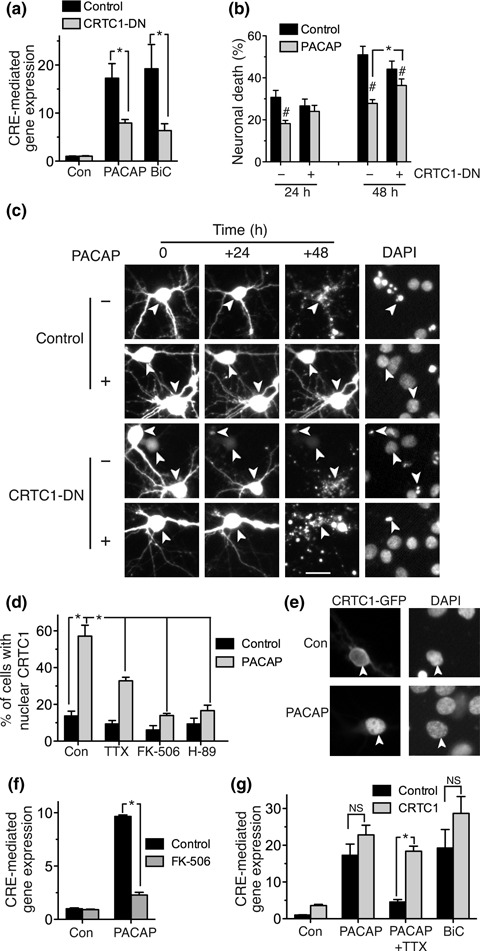
PACAP induces nuclear translocation of CRTC1, necessary for the AP firing-dependent component of CREB activation. (a) CRTC1 dominant negative inhibits PACAP mediated activation of CREB. Neurons were transfected with CRE-luciferase, pTK-Renilla and vectors encoding either a CRTC1 dominant negative mutant or control (β-globin). Neurons were stimulated PACAP or bicuculline plus 4-AP (BiC) (*p < 0.05, n = 4). (b,c) PACAP mediated long-lasting neuroprotection depends on CRTC1. The experimental protocol is the same as that illustrated schematically in Fig. 3(b). Briefly, neurons expressing GFP plus either CRTC1-DN (dominant negative) or β-globin control were treated ± PACAP 24 h post-transfection and then all cells were placed in TTX-containing medium after a further 24 h, at which point images of GFP-expressing neurons were taken. The fate of these cells was then monitored at 24 and 48 h after this medium change (*p < 0.05, paired T-test, n = 3; #p < 0.05, paired T-test comparing control to PACAP within each condition/timepoint). (c) shows example pictures. Scale bar = 20 μm. (d,e) PACAP induces CRTC1 nuclear translocation via activity-dependent calcineurin signaling. Neurons were transfected with a vector encoding GFP-tagged CRTC1. At 24 h post-transfection, neurons were treated with 20 ng/mL leptomycin B for 30 min to block nuclear export [to enable import to be observed more clearly (Kovacs et al. 2007)], plus the indicated inhibitors (1 μM TTX, 10 μM H-89 or 10 μM FK-506) and then PACAP added for 30 min prior to fixing of the cells and analysing localisation of GFP-CRTC1 in 400–800 cells per treatment (*p < 0.05, n = 4–8). (e) shows example pictures. (f) PACAP-induced activation of CRE-mediated gene expression requires the Ca2+-dependent phosphatase calcineurin. Where used, FK-506 was added 1 h prior to PACAP stimulation (*p < 0.05, n = 4). (g) CRTC1 over-expression rescues the inhibition of PACAP-mediated CRE activation by TTX. Neurons were transfected with CRE-luciferase, pTK-Renilla and either vectors encoding CRTC1 or β-globin control. 24 h post-transfection the neurons were stimulated with PACAP ± TTX or bicuculline + 4-AP (BiC) as indicated. Over-expression of CRTC1 does not further enhance CRE activation by BiC or PACAP, suggesting that levels are not limiting, however, it strongly enhances levels induced by PACAP in the presence of TTX (*p < 0.05, n = 4).
