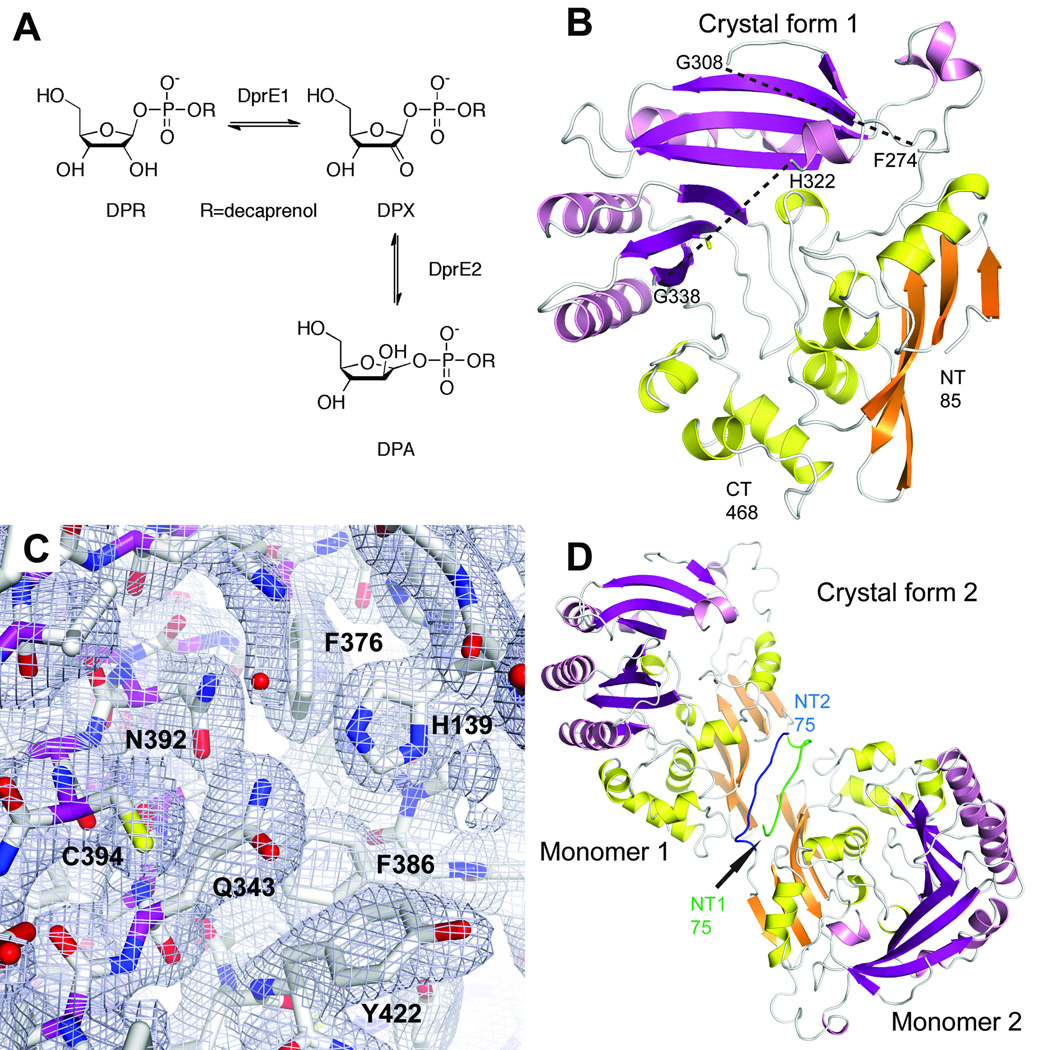
Figure 1. Overall structure of DprE1.
a. Oxidation of decaprenylphosphoryl-β-D-ribose (DPR) to decaprenylphosphoryl-2-keto-D-erythro-pentofuranose (DPX) catalyzed by DprE1 and further reduction of DPX to decaprenylphosphoryl-β-D-arabinose (DPA) by DprE2.
b. Cartoon representation of the DprE1 core structure in space group P3221. Secondary structure elements in the FAD-binding domain and in the substrate-binding domain are colored in orange and yellow and magenta and pink, respectively. The approximate positions of two mobile loop regions (between residues 274 and 308, and between residues 322 and 338) are indicated with dashes.
c. Final σA-weighted 2mFo-DFc electron density for the active site region in space group P3221.
d. Dimer formation in space group P21. The additional N-terminal residues 75–84 in the two monomers establish an antiparallel β-strand-like interaction. N-terminal residues from monomers 1 and 2 are colored in green and blue, respectively.