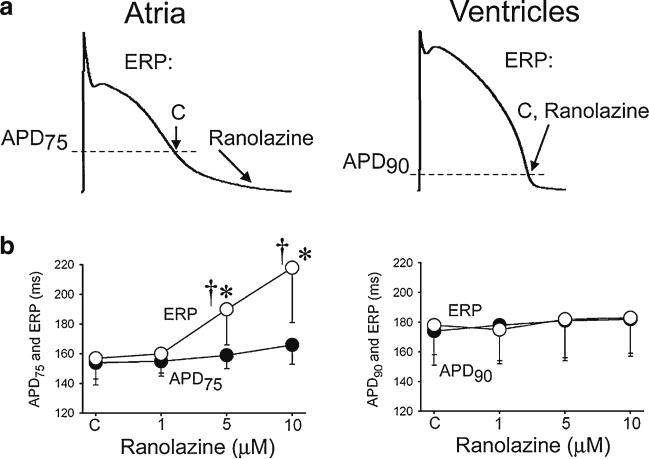
Fig. 5.
Ranolazine selectively induces prolongation of the effective refractory period (ERP) and development of post-repolarization refractoriness in atria (PRR, the difference between ERP and APD75 in atria and between ERP and APD90 in ventricles; ERP corresponds to APD75 in atria and APD90 in ventricles). CL=500 ms. C – control. The arrows in panel A illustrate the position on the action potential corresponding to the end of the ERP in atria and ventricles and the effect of ranolazine to shift the end of the ERP in atria but not ventricles. * p<0.05 vs. control. † = p<0.05 vs. APD75 values in atria and APD90 in ventricles; (n=5–18). From Burashnikov et al. [14], with permission. PRR is a peak INa-mediated parameter