Table 5. Effects of Substituents and pKa on Quantum Yieldsa for the Substituted pHP GABA 31 in Unbuffered H2O;b Entries Are Arranged in the Order of Decreasing pKa of the Substituted pHP Chromophore94.
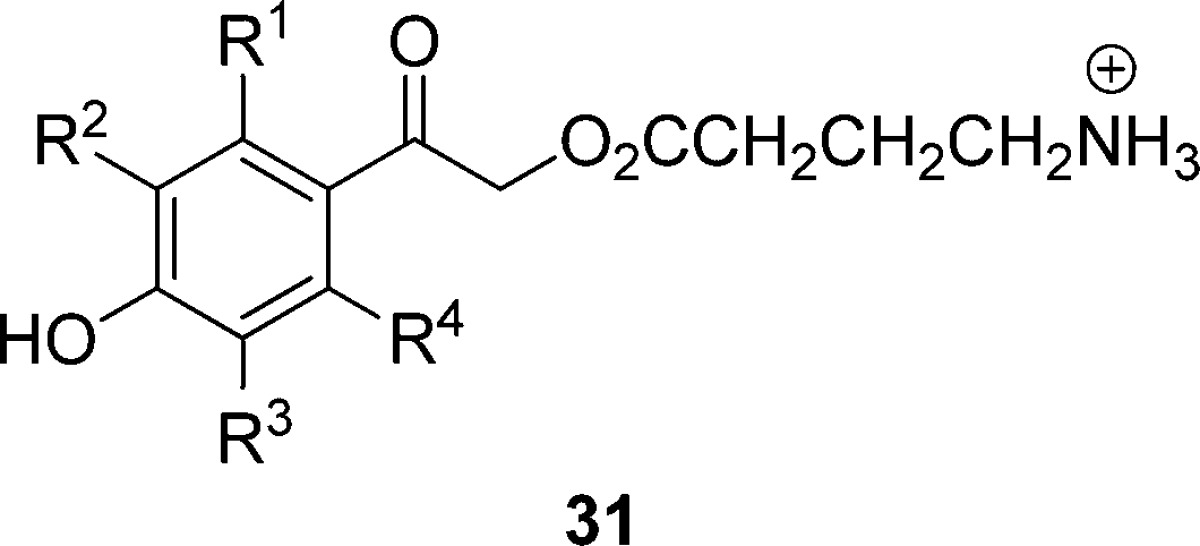
| 31 | pKa | Φdisc | ΦGABA | Φ (25)d | Φdis (Ac or DEP)d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3,5-CH3 | 8.2 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.13 | |
| 3-CH3 | 8.1 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.13 | |
| 2-CH3 | 8.0 | 0.11 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| 3-OCH3 | 7.9 | 0.07 | 0.06 | NDe | 0.39 (DEP) |
| R1–R4 = H | 7.8 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.30 (Ac) |
| 0.40 (DEP) | |||||
| 3,5-OCH3 | 7.8 | 0.03 | 0.03 | ND | 0.44 (DEP) |
| 2-F | 7.2 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.26 | |
| 2,6-F | 6.8 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.15 | |
| 3-F | 6.7 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.15 | |
| 3-OCF3 | 6.5 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.07 | |
| 2,3-diF | 5.9 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.22 | |
| 2,5-diF | 5.7 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.2 | |
| 3-CF3 | 5.5 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.14 | |
| 3,5-F | 5.3 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.1 | |
| 3-CN | 5.2 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.39 | 0.17 (Ac) |
| 2,3,5-triF | 4.5 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.06 | |
| tetra-F | 3.9 | 0.11 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
All runs were low conversions to products (<5%); standard deviations were < ±0.02.
Unbuffered 18 MΩ ultrapure H2O.
Disappearance quantum yield when GABA is the leaving group.
Quantum yield for the substituted phenylacetic acid (25).
Disappearance quantum yield when Ac (acetate) or DEP (diethyl phosphate) is the leaving group.
ND = not determined.94
