FIG. 8.
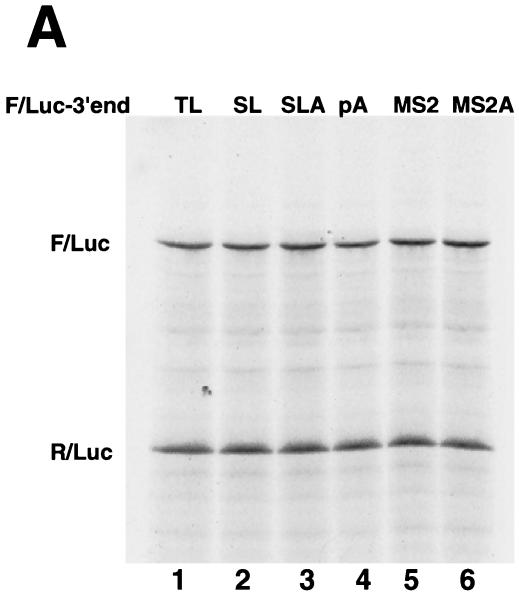
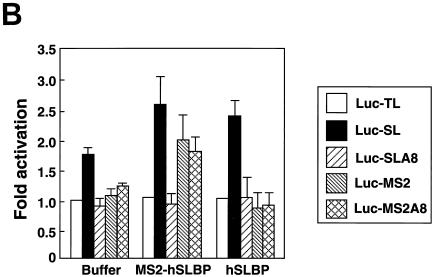
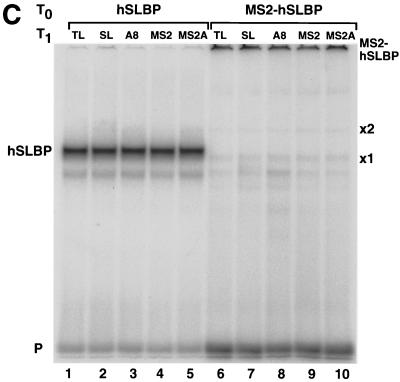
The MS2-hSLBP protein activates translation of the Luc-MS2A8 mRNA but not the Luc-SLA8 mRNA. (A) Capped luciferase reporter mRNAs (Luc-TL, lane 1; Luc-SL, lane 2; Luc-SLA8, lane 3; Luc-pA, lane 4; Luc-MS2, lane 5; Luc-MS2A8, lane 6) were mixed with equal amounts of the R-Luc-SL mRNA and translated in a reticulocyte lysate in the presence of [35S]methionine. The products were resolved by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and detected by autoradiography. The constructs are those shown in Fig. 4A (except for Luc-pA, which contains a 50-nt poly(A) tail) (25). SL, stem-loop; F/Luc, firefly luciferase; R/Luc, Renilla luciferase. (B) Xenopus oocytes were injected with buffer or with synthetic mRNAs encoding hSLBP, a MS2-hSLBP fusion protein, or the MS2 protein. At 16 h later the reporter mRNAs (Luc-TL, Luc-SL, Luc-SLA8, Luc-SLMS2, and Luc-MS2A8) analyzed as described for panel A were injected, and the oocytes were incubated for an additional 16 h. The oocytes were harvested, and luciferase activity levels were determined, with the activity of Luc-TL set at 1. The averages of the results of two independent experiments using different frogs are shown. (C) The extracts (described for panel B) from oocytes containing the reporter mRNAs indicated at the top of each lane and expressing either human SLBP (lanes 1 to 5) or the MS2-hSLBP fusion protein (lanes 6 to 10) were incubated with the radiolabeled stem-loop probe, and the complexes were resolved by native gel electrophoresis. The positions of the endogenous xSLBP1 and xSLBP2 complexes are indicated by x1 and x2. Because of the large size of the MS2-hSLBP fusion protein, the complex migrates near the top of the gel.